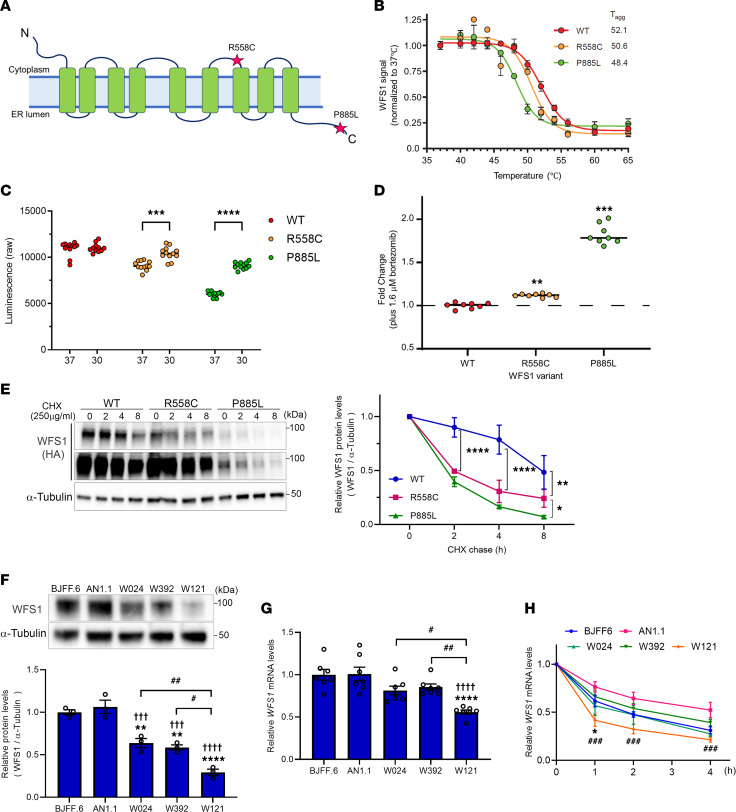
Figure 2. WFS1 p.R558C is more stable in the cell compared with p.P885L variant.
(A) Diagram of WFS1 protein showing the location of 2 variants, R558C and P885L. (B) Thermal profiles of WFS1 variants (WT, R558C, and P885L) measured using SplitLuc-tagged reporters expressed in HEK293T cells (data from 3 independent experiments). (C) Luminescence intensities of WFS1 variants in cells incubated at 30°C and 37°C for 24 hours (n = 12, ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001 by unpaired t test). (D) Fold change of luminescence intensities of WFS1 variants treated with a proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib, for 24 hours (**P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 by unpaired t test compared with untreated). (E) (Left) Representative blotting image of WFS1 (HA) and α-Tubulin in CHX chase assay. Lower panel of WFS1 (HA) is long-exposure image. (Right) A quantification of relative WFS1 protein level normalized with α-Tubulin. (n =3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ****P < 0.0001 by 2-way ANOVA.) (F) (Upper) Representative blotting image of WFS1 and α-Tubulin in iPSCs. (Lower) Quantification of relative WFS1 protein level normalized with α-Tubulin (n = 3, **P < 0.01 and ****P < 0.0001 by 1-way ANOVA compared with BJFF.6, †††P < 0.001 and ††††P < 0.0001 by 1-way ANOVA compared with AN1.1, #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 by 1-way ANOVA). (G) Relative mRNA level of WFS1 in iPSCs. (n = 7, ****P < 0.0001 by 1-way ANOVA compared with BJFF.6, ††††P < 0.0001 by 1-way ANOVA compared with AN1.1, #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 by 1-way ANOVA.) (H) Relative mRNA level of WFS1 in ActD chase assay (n = 3, *P < 0.05 by 1-way ANOVA compared with BJFF.6, ###P < 0.001 by 1-way ANOVA compared with AN1.1).