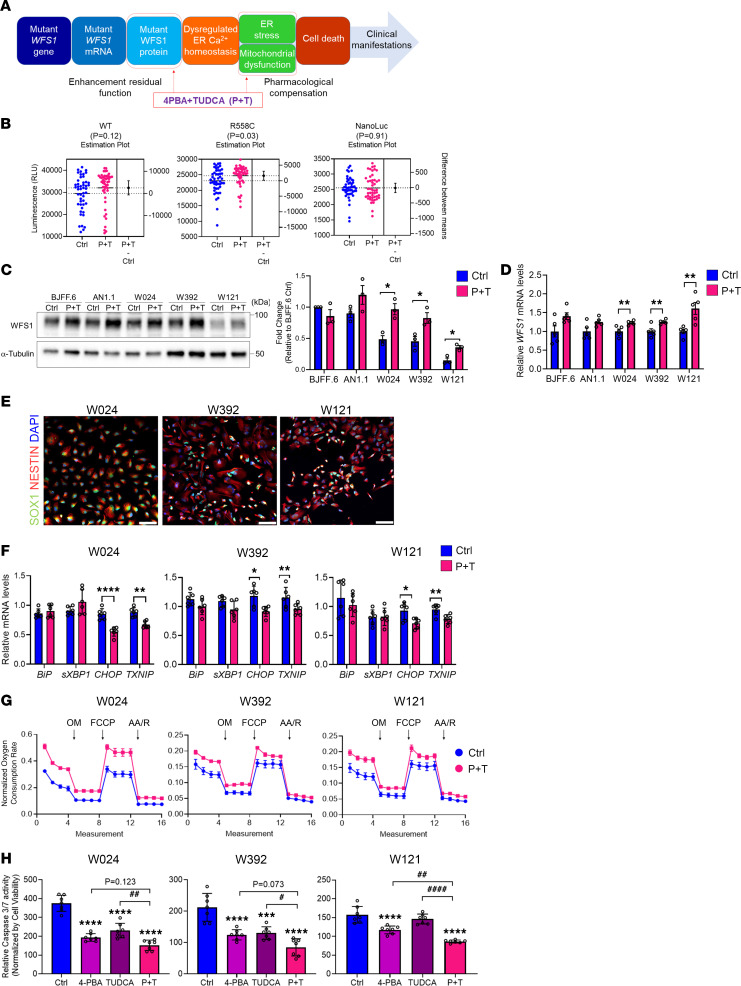
Figure 3. A combination treatment with 4-PBA and TUDCA mitigates detrimental effect of WFS1 c.1672C>T, p.R558C variant.
(A) A schematic of Wolfram syndrome etiology and the targets to modulate by a combination treatment of 4-PBA and TUDCA (P+T). (B) Expression of HiBiT-tagged WFS1 protein after treatment with 500 μM 4-PBA and 50 μM TUDCA (P+T) for 24 hours. NanoLuc levels, expressed from an identical plasmid backbone, were examined (n = 48, P value by unpaired t test). (C) (Left) Representative blotting images of WFS1 and α-Tubulin in iPSCs treated with or without P+T for 48 hours. (Right) Quantification of WFS1 protein levels normalized with α-Tubulin. (n = 3, *P < 0.05 by unpaired t test compared with Ctrl.) (D) Relative mRNA levels of WFS1 in iPSCs treated with or without P+T for 48 hours (n = 5, **P < 0.01 by unpaired t test compared with Ctrl). (E) Representative immunofluorescence images of neural progenitor cell (NPC) markers in NPCs differentiated from patient-derived iPSCs. Scale bar: 100 μm. (F) Quantitative PCR analysis of ER stress–related genes in NPCs treated with or without P+T for 48 hours. (n = 6, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ****P < 0.0001 by unpaired t test compared with Ctrl.) (G) Mitochondrial respiration of NPCs treated with or without P+T for 48 hours represented as percentage of baseline oxygen consumption rate (OCR) measurements. Respiration was interrogated by measuring changes in relative OCR multiple times, every 8.5 minutes, after injection with oligomycin (OM), FCCP, and antimycin A (AA)/rotenone (R) (n = 3, W024: ***P < 0.001, W392: *P < 0.05, and W121: *P < 0.05 by unpaired t test compared with Ctrl AUC). (H) Caspase-3/7 activity normalized by cell viability in NPCs treated with or without either of 4-PBA, TUDCA, or P+T for 48 hours. (n = 7; ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001 by 1-way ANOVA compared with Ctrl; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ####P < 0.0001 by 1-way ANOVA.)