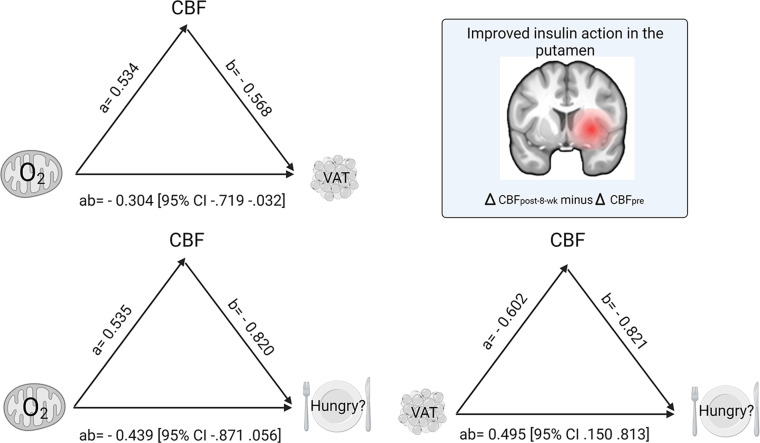
Figure 5. Model of exercise-promoted central insulin action as a mediator between changes in peripheral metabolism and central insulin modulated feeling of hunger from before to after an 8-week exercise intervention.
Path coefficients and CIs are shown next to arrows. All variables relate to changes from before to after the 8-week exercise intervention. Brain template at the top right of the graph shows region in the striatum (i.e., right putamen), revealing a significant exercise-induced increase in central insulin action (ΔCBFpost-8-week – ΔCBF pre). In the model on the top left, path ab indicates the indirect effect of the change in maximal coupled mitochondrial respiration in skeletal muscle fibers on the change in VAT via the exercise-induced change in putamen insulin action. In the model on the bottom left, path ab indicates the indirect effect of the change in maximal coupled mitochondrial respiration in skeletal muscle fibers on the change in hunger (ΔVASpost-8-week – ΔVASpre) via the exercise-induced change in right putamen insulin action. In the model on the bottom right, path ab indicates the indirect effect of the change in VAT on hunger via the exercise-induced change in putamen insulin action. CBF, cerebral blood flow; O2, oxygen flux for mitochondrial respiration; VAS, visual analogue scale for hunger ratings; VAT, visceral adipose tissue.