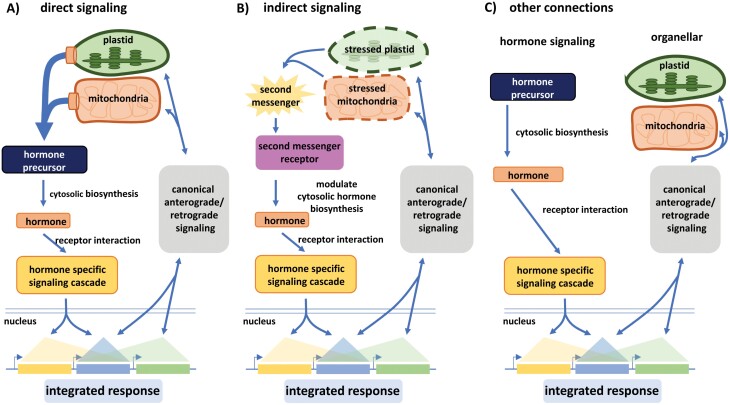
Fig. 2.
Direct/indirect signals in regulation of gene expression. Different types of connections between organelles and hormone signaling affect gene expression. (A) Direct signals: hormone levels, depending on precursor metabolites for hormone biosynthesis of exclusive organellar origin, regulate a subset of genes (yellow) while another subset of genes is controlled by retrograde signals from organelles (green), and a third subset of genes is regulated by both input pathways (blue). (B) Indirect signals: hormone levels regulating a subset of genes are indirectly altered via second messenger molecules of organellar origin, modulating the enzymes relevant for hormone biosynthesis. (C) Other signaling connections: transcriptional changes that do not fall into (A, B) but require a functional hormonal signaling cascade and a functional organellar retrograde signaling cascade at the same time.