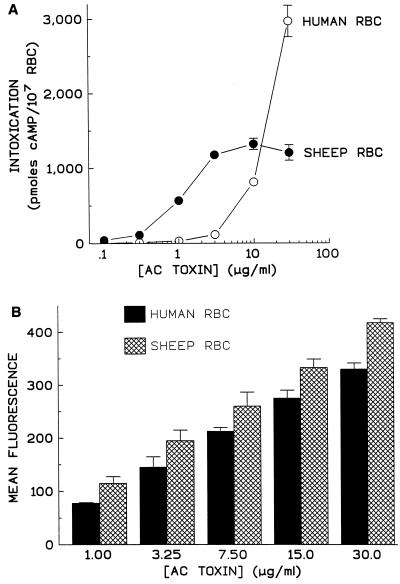
FIG. 7.
While AC toxin exhibits reduced potency in its ability to increase cAMP in human RBC, there is only a modest reduction in binding of the toxin to these cells. Human and sheep blood was drawn the day of the experiment, and RBC were isolated and washed as described in Materials and Methods and then incubated with AC toxin at indicated concentrations for 30 min at 37°C. (A) Intracellular cAMP was measured as described in Materials and Methods. Data represent the mean and standard deviation of triplicate samples from a single experiment representative of three separate experiments. (B) Binding of AC toxin to sheep and human RBC was measured as described in Materials and Methods. Data are expressed as mean fluorescence minus background and represent the mean ± standard deviation from three similar experiments.