Figure 4. ATP13A1 facilitates type II membrane protein topogenesis.
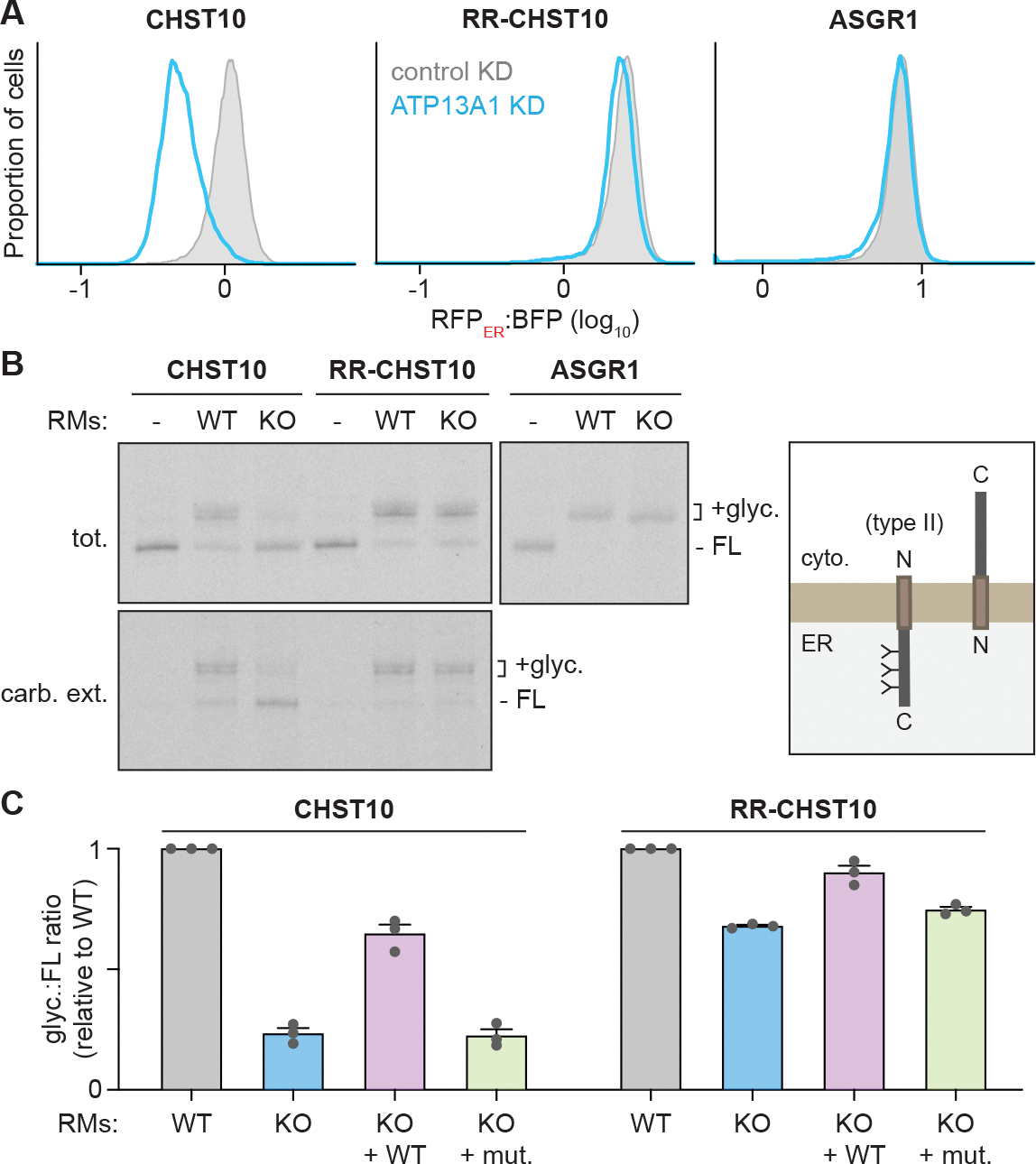
(A) ATP13A1 is required for CHST10 stability. RFPER:BFP ratios of wildtype CHST10 (left), RR-CHST10 (middle), or ASGR1 (right) type II protein topology reporters in wildtype cells treated with control siRNAs (control KD; gray; same samples as Figure 3D) or siRNAs against ATP13A1 (ATP13A1 KD; light blue).
(B) Reconstitution of ATP13A1-dependent CHST10 topogenesis. SDS-PAGE and autoradiography (left) of radiolabeled CHST10, RR-CHST10, or ASGR1 synthesized in vitro without or with ER-derived rough microsomes (RMs) isolated from wildtype (WT) or ATP13A1 knockout (KO) cells before (tot.) or after carbonate extraction (carb. ext.) to isolate membrane-embedded populations. All proteins contain N-glycosylation sites that are modified in the correct type II topology (right) and a C-terminal FLAG tag used for denaturing immunoprecipitations. FL, full-length substrate; +glyc, glycosylated substrate.
(C) Glyc.:FL ratios (mean ± sem) of CHST10 (left) or RR-CHST10 (right) in insertion assays as in (B) containing RMs derived from WT, ATP13A1 KO, or ATP13A1 KO cells re-expressing WT or catalytically inactive (D533A; mut.) ATP13A1, normalized to reactions containing WT RMs for 3 replicates.
See also Figure S5.
