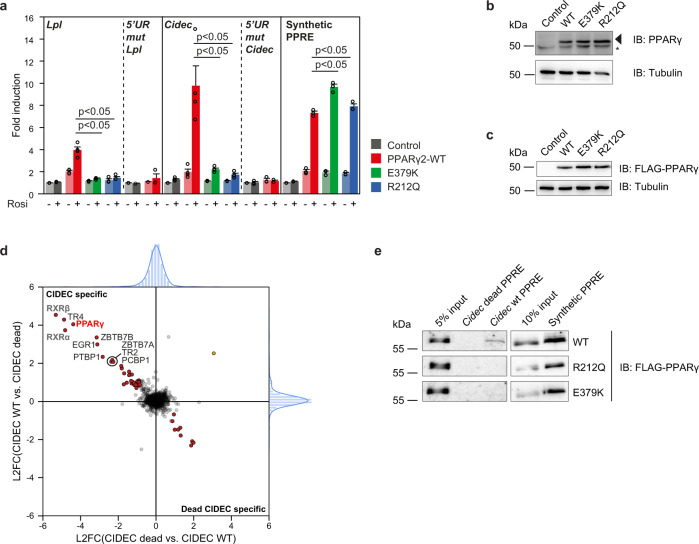
Fig. 2. E379K and R212Q mutants destabilize PPARγ:RXR binding to DNA in vitro.
a U2OS cells were transiently cotransfected with expression vectors encoding PPARγ-WT or mutants and different reporter constructs as indicated, in the absence or presence of 1 µM rosiglitazone. Activation of the reporter is expressed as fold induction over that with empty vector (control). Data are presented as mean values + SEM, with individual data points indicated with circles, n = 3–4 biologically independent experiments. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons were used to compare cells transfected with mutant vs. WT; *p < 0.05 cells transfected with mutant vs. WT. b Expression of the different PPARγ proteins transiently overexpressed in U2OS cells, as assessed by western blot. The arrow indicates PPARγ, and the asterisk indicates a non-specific band. Control, empty vector control; WT, PPARγ wild-type. Three independent experiments were performed and similar results were obtained. c Expression of the different FLAG-tagged PPARγ proteins stably overexpressed in U2OS cells, as assessed by western blot using a FLAG-tag antibody. Control, empty vector control; WT, wild-type. Three independent experiments were performed and similar results were obtained. d DNA affinity purification-mass spectrometry analysis of Cidec PPRE interactors. Forward and reverse experiments were performed using oligonucleotides containing the Cidec PPRE motif or a mutant version (Cidec dead), followed by dimethyl labeling and mass spectrometry analysis. Log2 ratios (L2FC) of all identified and quantified proteins (from nuclear extracts) in both experiments were plotted against each other. Proteins binding equally well to both oligonucleotides center around log2(ratio) = 0 and are marked in light gray. Proteins binding significantly better to the Cidec PPRE motif or the Cidec dead motif were determined by outlier statistics. These proteins are marked in red. e DNA affinity purification followed by western blot analysis were performed using oligonucleotides containing the Cidec PPRE motif, the Cidec dead motif and the synthetic PPRE motif. Pulldowns were performed using nuclear extracts containing the different FLAG-tagged PPARγ proteins. Three independent experiments were performed, and similar results were obtained. Source data for panel a–c and e are provided in the Source Data file.