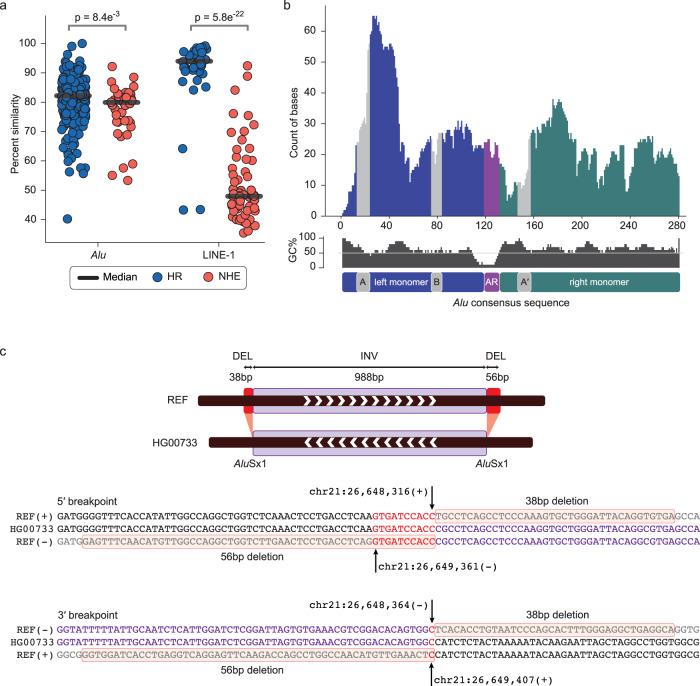
Fig. 3. Features and complexities of TEMRs.
a Median similarity between TEs at TEMR breakpoints differs by TE type and mechanism (TEMR-HR: 354 Alu and 36 LINE-1 and TEMR-NHE: 43 Alu and 60 LINE-1). A two-sided Welch’s t-test was used to calculate the p-value. HR, homologous recombination; NHE, non-homologous repair; TE, transposable element; SV, structural variant; MEI, mobile element insertion, TEMR, transposable element-mediated rearrangement; LINE; long interspersed nuclear element. b Distribution of the breakpoint microhomology along the Alu consensus sequence. Alu elements consist of a left monomer (indigo), right monomer (green), RNA polymerase III promoter regions (gray A-Box, B-Box and A′-Box) and Adenosine Rich region (AR, purple). c Example of a 988 bp TEMR inversion (INV) with additional complex breakpoints (38 bp and 56 bp deletion (DEL) indicated in pink shaded sections) implicating replication-based mechanisms of variant formation. REF, reference genome (GRCh38).