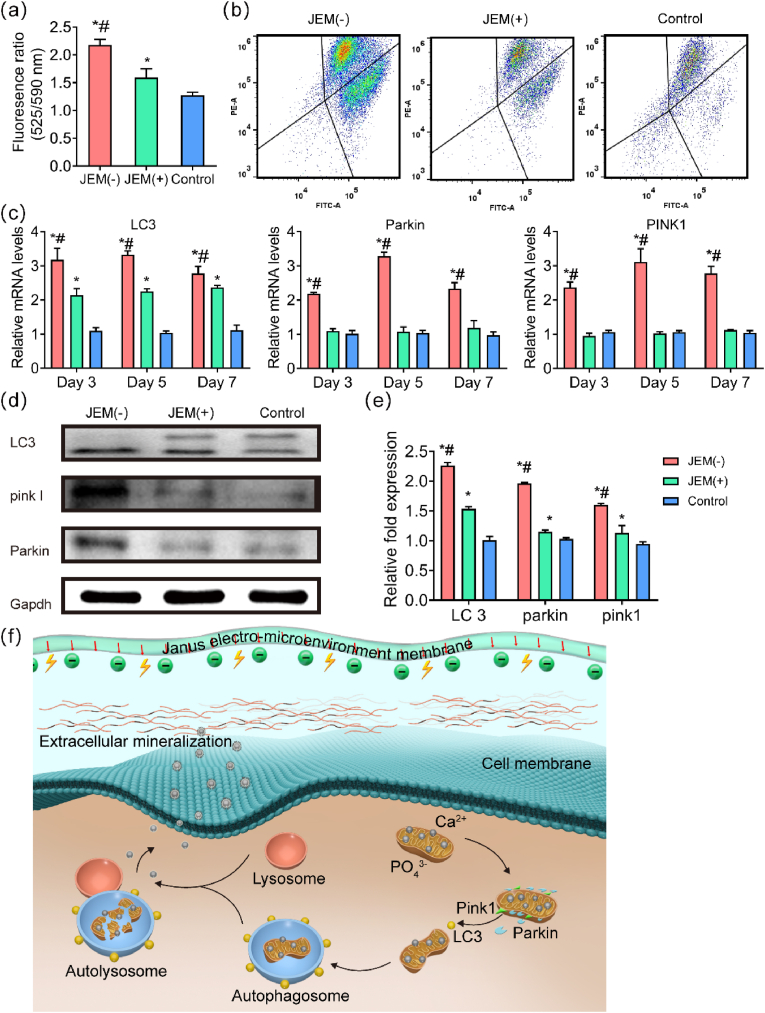
Fig. 7.
Evaluation of mitophagy in rBMSCs on JEM membranes. (a and b) Quantitative analysis of changes in mitochondrial membrane potential in rBMSCs at 7 days, n = 6. (c) qRT-PCR analysis of mitophagy-related gene expression (LC3 II, Pink I, and Parkin) in rBMSCs on JEM(+), JEM(−), and control membranes at 3, 5, and 7 days, n = 9. (d and e) Western blot of mitophagy-related proteins (LC3 II, PINK I, and PARKIN) in rBMSCs on JEM(+), JEM(−), and control membranes at 14 days, n = 6. (f) Schematic illustration of mitophagy induced by the JEM(−) membrane. When the JEM(−) membrane interacts with rBMSCs, the mitochondria swell and lose their membrane potential, activating PINK1-PARKIN-mediated mitophagy. The damaged mitochondria are digested by autolysosomes and release intramitochondrial mineral particles into the extracellular matrix, which promotes mineralization. ∗p < 0.05, compared with Control; #p < 0.05, compared with JEM(+). Statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) were measured using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) combined with the Student–Newman–Keuls (SNK) multiple comparison post hoc test.