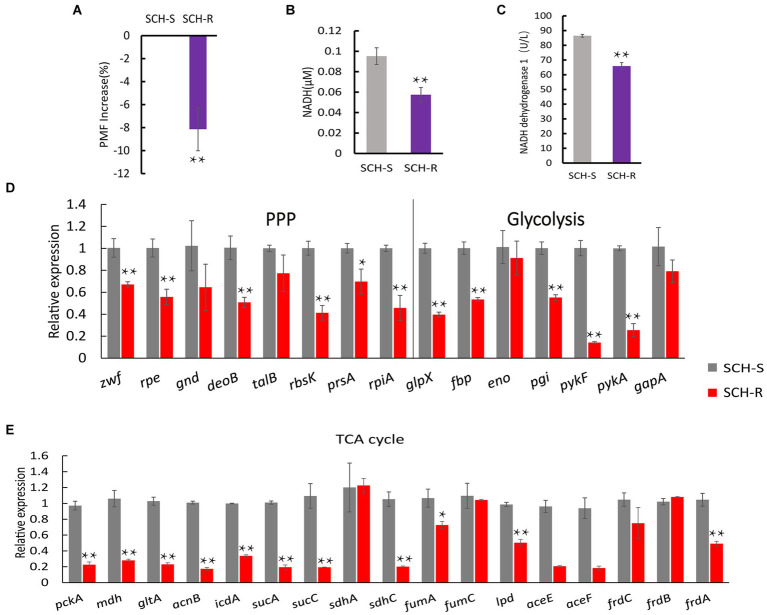
Figure 3.
SCH-R resistance is mediated by disrupted central carbon metabolism. (A) Variation of the PMF in SCH-R and SCH-S. (B) NADH concentration in SCH-R and SCH-S. (C) Activity of NADH dehydrogenase 1 in SCH-R and SCH-S. (D,E) QRT-PCR for the expression of key genes in central carbon metabolism. pckA, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; mdh, malate dehydrogenase; gltA, citrate synthase; acnB, aconitate hydratase 2; icdA, isocitrate dehydrogenase; sucA, 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase E1 component; sucC, succinyl-CoA synthetase beta subunit; sdhA, succinate dehydrogenase; sdhC, succinate dehydrogenase; fumA, fumarate hydratase, class I; fumC, fumarate hydratase, class II; lpd, dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase; aceE, pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component; aceF, pyruvate dehydrogenase E2 component; frdC, fumarate reductase subunit C; frdB, fumarate reductase iron–sulfur subunit; frdA, fumarate reductase flavoprotein subunit; zwf, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; rpe, ribulose-phosphate 3-epimerase; gnd, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase; deoB, phosphopentomutase; talB, transaldolase; rbsK, ribokinase; prsA, ribose-phosphate pyrophosphokinase; rpiA, ribose 5-phosphate isomerase A; glpX, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase II; fbp, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase I; eno, phosphopyruvate hydratase; pgi, glucose-6-phosphate isomerase; pykF, pyruvate kinase; pykA, pyruvate kinase; gapA, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Results are displayed as the mean ± SEM and three biological repeats are carried out. Significant differences are identified (*p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01).