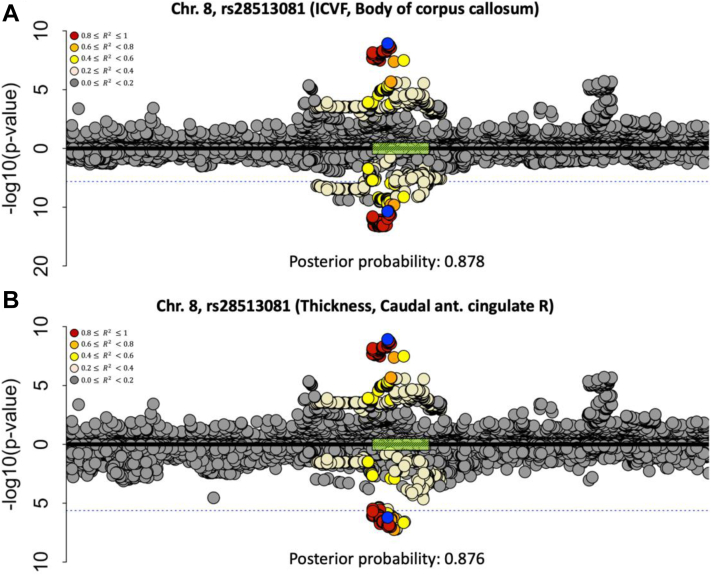
Fig. 4.
Co-localisation of the two most significantly associated IDPs with chromosome 8 (region around the DEPTOR gene), against IPF risk.(a) Against a white matter microstructure feature (ICVF of the body of corpus callosum), (b) Against a cortical feature (cortical thickness of the caudal anterior cingulate RH). Chromosome 8: 119,934,133–121,934,069 build x-axis for both plots. Each point represents a genetic variant with chromosomal position on the x-axis and −log(P-value) on the y-axis. The GWAS data for IPF risk is presented above the x-axis, and the GWAS data for the IDP is shown below the x-axis. The sentinel variant from the IPF GWAS is shown in blue and other variants are coloured by their linkage disequilibrium with the IPF GWAS sentinel. The dashed blue lines indicate the Bonferroni threshold (2.36 × 10−6). The green box on the x-axis demonstrates the position of the DEPTOR gene. To show the GWAS data for IPF risk, we used the variant summary data of the discovery stage (including three independent IPF case–control collections (named the UK, Chicago, and Colorado studies comprised up to 2668 IPF cases and 8951 controls) of the study by Allen et al.5 The R2 is calculated from the actual cohort.