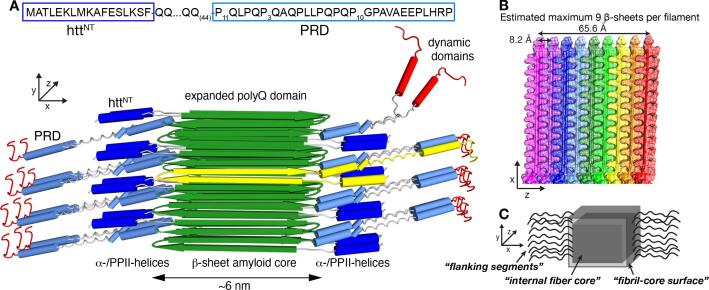
Fig. 1.
Fibril architecture of aggregated mutant HttEx1. (A) Sequence and structural model of HttEx1 fibers. The xyz axes indicate the fiber growth direction (y), fiber width (x) and fiber depth (z). The yellow β-hairpin structure shows a monomer, which is exposed on the front side of the fibril core. (B) Structural model of HttEx1 fibers showing the layering of β-sheets in the z direction. Each β-sheet is shown in different colour, with a 6–7 nm protofilament core composed of around nine stacked β-sheets. (C) Schematic drawing of the fibril structure, marking the nomenclature distinguishing the internal fiber core (i.e. dry interfaces), fibril core surface (Eisenberg “wet interface”), as well as the solvent exposed flanking domains. Panels A-B adapted with permission from ref. (Lin et al., 2017) and (Boatz et al., 2020), under the Creative Commons CC-BY license. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)