Figure 8.
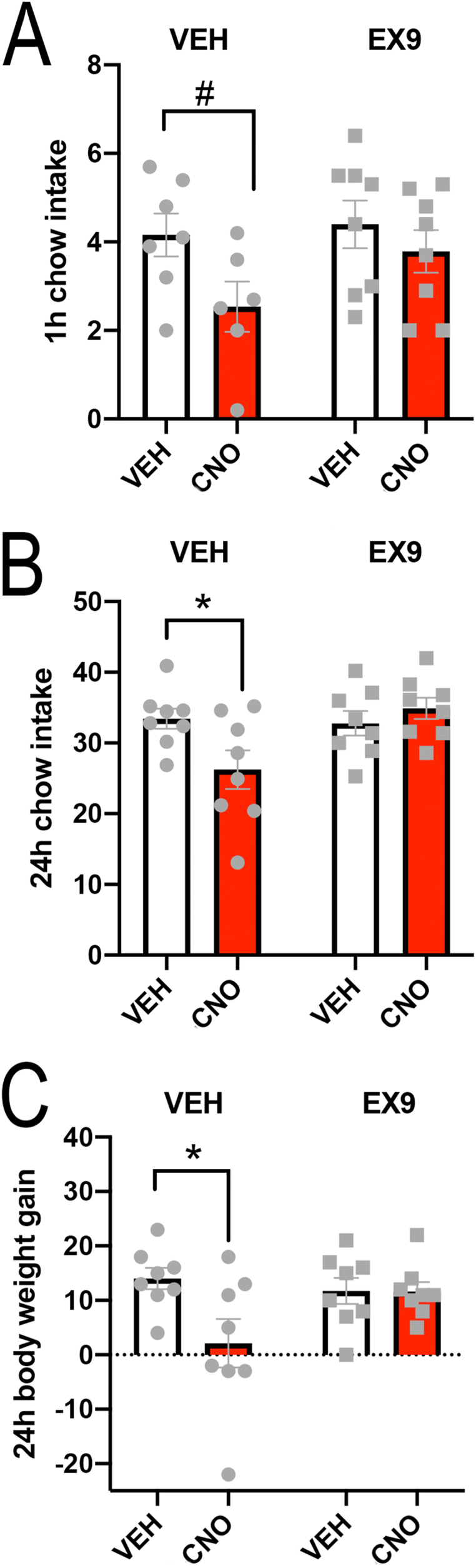
Central Exendin-9 (Ex9; a GLP1R antagonist) blockade of the hypophagic effect of central CNO. Male Gcg-Cre Het rats with prior cNTS-targeted delivery of AAV expressing Cre-dependent GqDREADD were used to determine whether central (LV-delivered) CNO suppresses dark-onset chow intake, and if so, whether this effect depends on central GLP1R signaling. A, 1 h chow intake was not significantly reduced by LV administration of vehicle followed by either LV vehicle or LV CNO, although a trend for CNO to suppress 1 h intake was evident. B, 24 h chow intake was significantly reduced when LV vehicle was followed by LV delivery of CNO (∗P < 0.05), and this 24 h hypophagic effect was completely blocked by LV delivery of CNO was preceded by LV delivery of Ex9. C, CNO reduced body weight gain at the 24 h timepoint in rats pretreated with vehicle, but not in rats pretreated with EX9 before CNO.
