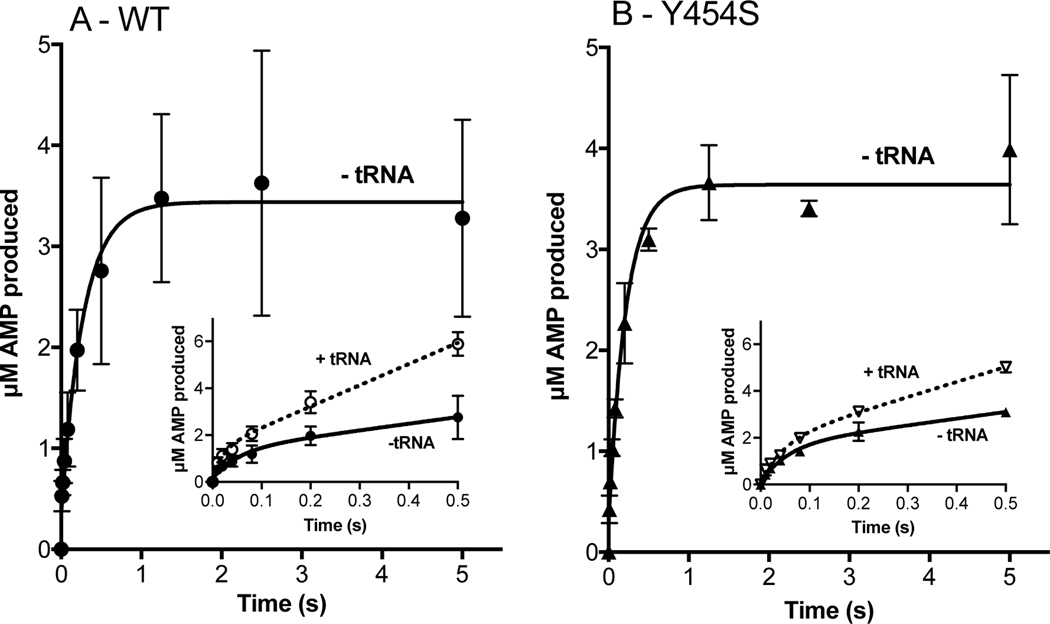
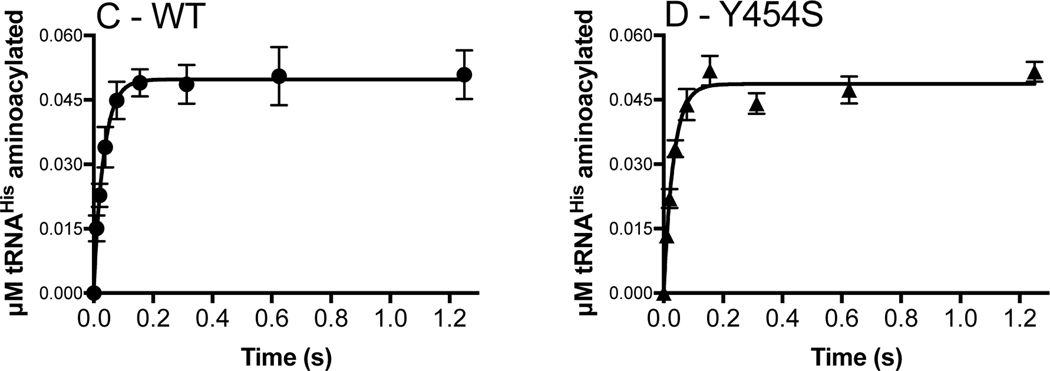
Figure 3.
Amino acid activation and the rate of histidine transfer is unaffected by the Y454S mutation even in the presence of tRNAHis. Amino acid activation (WT: panel A; Y454S: panel B) was monitored by mixing 5 μM monomer HARS enzyme (WT: filled circles; Y454S: filled triangles) with 100 μM ATP and saturating histidine. tRNAHis (25 μM) addition (empty circles and empty triangles, insets: note 0.5 s time scale) increased the rate of amino acid activation, which was determined by linear fit within the first turnover. The rate constant for histidine transfer ktrans (WT: panel C; Y454S: panel D) was determined by single turnover with 2 μM enzyme, preformed with histidyl-adenylate, and mixed with 100 nM tRNAHis. ktrans was determined by fit to a single exponential. The number of experiments is reported in Tables 2 and 3.