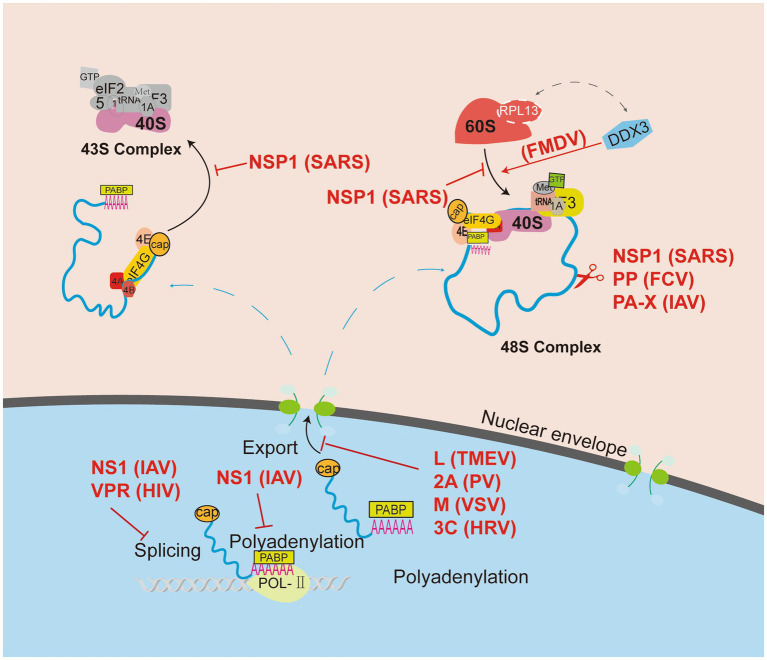
Figure 1.
Viruses manipulate ribosomes to shut down host protein translation. Cellular mRNA biogenesis begins in the nucleus, and viruses use various mechanisms to block the translation of host mRNA, including remodeling of the host mRNA library, inhibiting host mRNA transport from the nucleus, and blocking ribosomal recruitment of eukaryotic translation initiation factor (eIF). Consequently, viruses can block ribosomal mRNA entry channels or inhibit the binding of ribosomal size subunits to prevent the translation of host proteins.