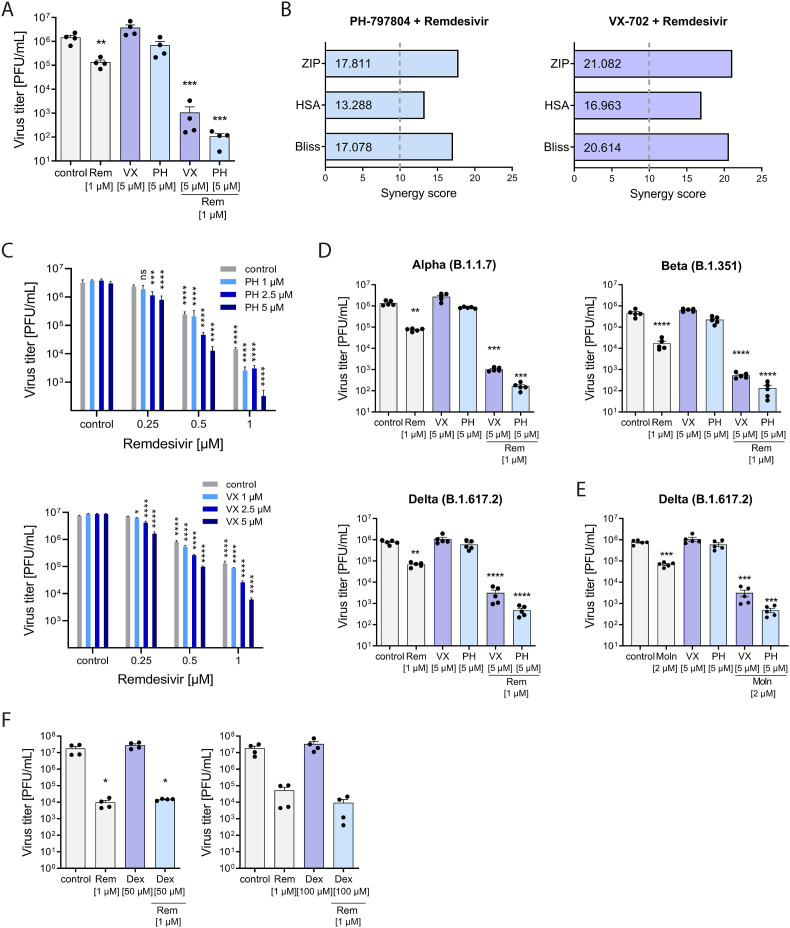
Fig. 6.
PH and VX synergistically reduce viral replication during co-treatment with the direct acting antiviral drugs Remdesivir and Molnupiravir. Calu-3 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of PH, VX, Dexamethasone or DMSO 1 h prior to viral infection with MOI 0.01 and until sample harvest. Remdesivir (1 μM) and Molnupiravir (1 μM) were added 1 h p.i. A) Production of infectious virus particles was determined by plaque assay and expressed as PFU/ml. Statistical significance was calculated by one way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test (n = 4). B) Synergy scores for both drug pairs were calculated using the indicated reference drug interaction models. Score values above 10 are considered as synergistic. C) Production of infectious virus particles for the indicated drug combinations was determined by plaque assay and expressed as PFU/ml. Statistical significance was calculated by two-way-ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test (n = 4). Calu-3 cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern Alpha, Beta or Delta at MOI 0.01 and treated with D) Remdesivir (Rem) or E) Molnupiravir (Moln) at the indicated concentrations for 48 h. Data are expressed as PFU/ml, bars indicate means ± SEM; n = 5/treatment. Statistical significance was determined using one way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test. F) Combination treatment of Dexamethasone (Dex, 50 μM and 100 μM) and Remdesivir (1 μM). Production of infectious virus particles was determined by plaque assay and expressed as PFU/ml. Statistical significance was calculated by one way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test (n = 4). *p < 0.05, **p ≤ 0.05, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001.