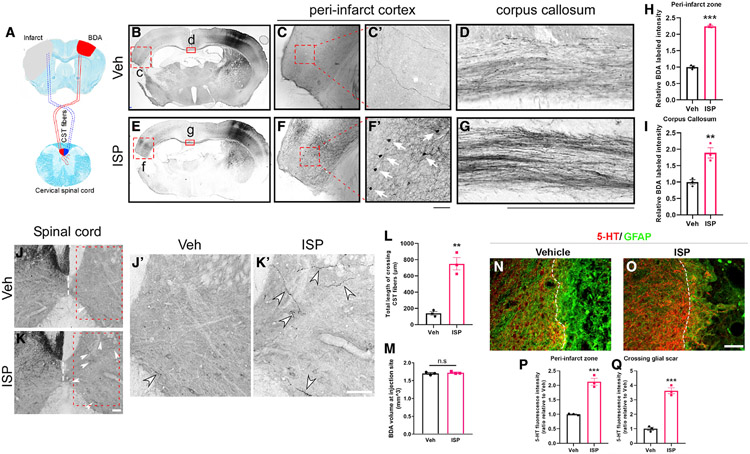
Figure 4. Post-stroke ISP treatment enhances axonal sprouting from the contralateral cortex after stroke.
(A) Schematic representation of the BDA injection site (contralateral to stroke side) and corticospinal tract (CST).
(B–M) ISP enhances contralateral cross-callosal projections to the stroke side (B–D, vehicle (Veh)-treated stroke mice; E–G, ISP-treated stroke mice). Quantification in (H) and (I). ISP-treated mice show more callosal projecting neuronal cell bodies retrogradely labeled by BDA directly adjacent to the lesion. (C and F and higher magnification shown in C′ and F′). ISP also enhances the corticospinal tract (CST) sprouting from the non-stroke cortex to the contralateral side across the midline of the cervical spinal cord (J and K and J′ and K′ showing higher magnification). Quantification for CST cross-midline sprouting in (L). Note that BDA injection volume at the non-stroke cortex is similar in Veh or ISP-treated mice (representative images in B and E and quantification in M).
(N and O) ISP treatment enhances the density of 5-HT+ axons that are in the peri-infarct area and crossing the glial scar region (quantification shown in P and Q). Scale bar: 100 μm (n = 3 mice for each group; multiple brain and spinal cord sections were analyzed for each mouse, and average was used as a single data point for statistical analysis). **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001, Student’s t test.