Figure 3.
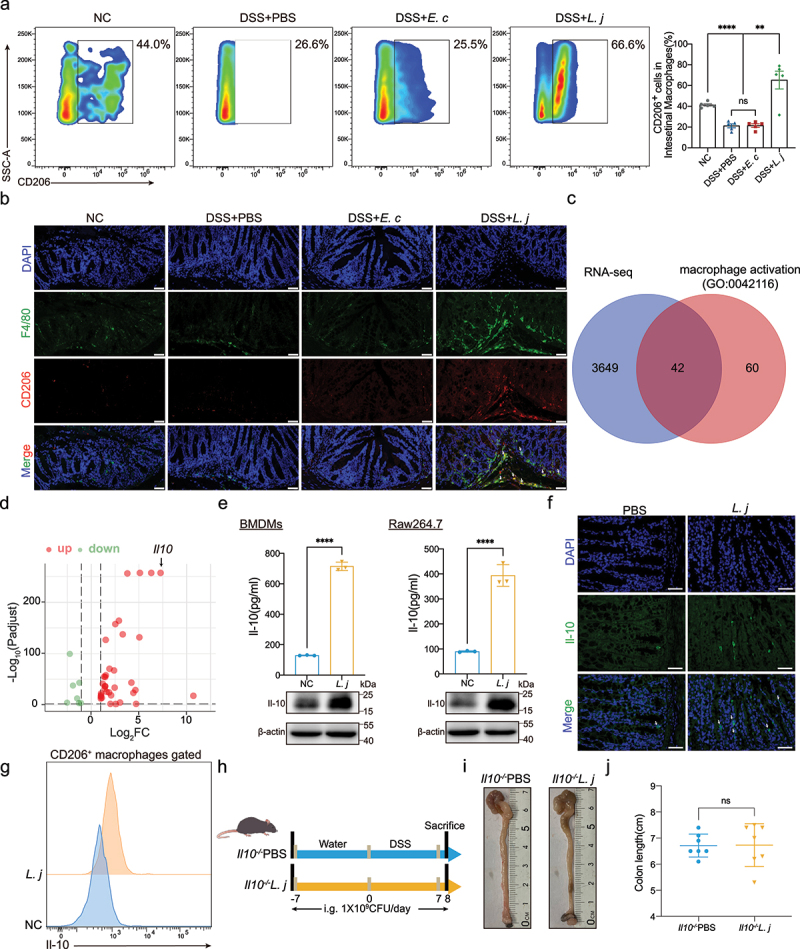
L. johnsonii promoted CD206+ macrophagesIL-10 activation in vivo and in vitro.
a, Flow cytometry representation of CD206+ macrophages from colon lamina propria in chronic colitis model. b, Representative images of immunofluorescence staining of CD206+ macrophages (dual F4/80+ CD206+) in chronic colitis mice. Scale bars, 50 µm. The white arrows indicated the positive stained cells. c, Venn diagram showed the intersecting of the RNA sequencing results and the macrophage activation gene set (GO:0042116). d, Volcano map of the differential gene expression patterns (Figure 3c) (n = 3 per group, fold change>2, logCPM>2, FDR<0.05). e, The protein expression of Il-10 of PBS control (NC) or L. johnsonii (L. j) treated BMDMs and Raw264.7 cells were examined by ELISA and western blot. f, Representative images of immunofluorescence staining of Il-10 in colon tissues of PBS control (PBS) or L. johnsonii (L. j) treated chronic colitis mice. Scale bars, 100 µm. The white arrows indicated the positive stained cells. g, Representative histograms of Il-10 expression by CD206+ macrophages were shown. h, Schematic diagram showing that the process of DSS-induced acute colitis in Il10−/− mice. i, Representative colon images of the groups with gavaging PBS (Il10−/−PBS), gavaging L. johnsonii (Il10−/−L. j). j, Colon length was analyzed in two groups. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 5–7. **, P < .01; ****, P < .0001; ns no significant. ANOVA test (a), unpaired Student’s t test (e, j).
