Fig. 5 |. TIL-B effector mechanisms.
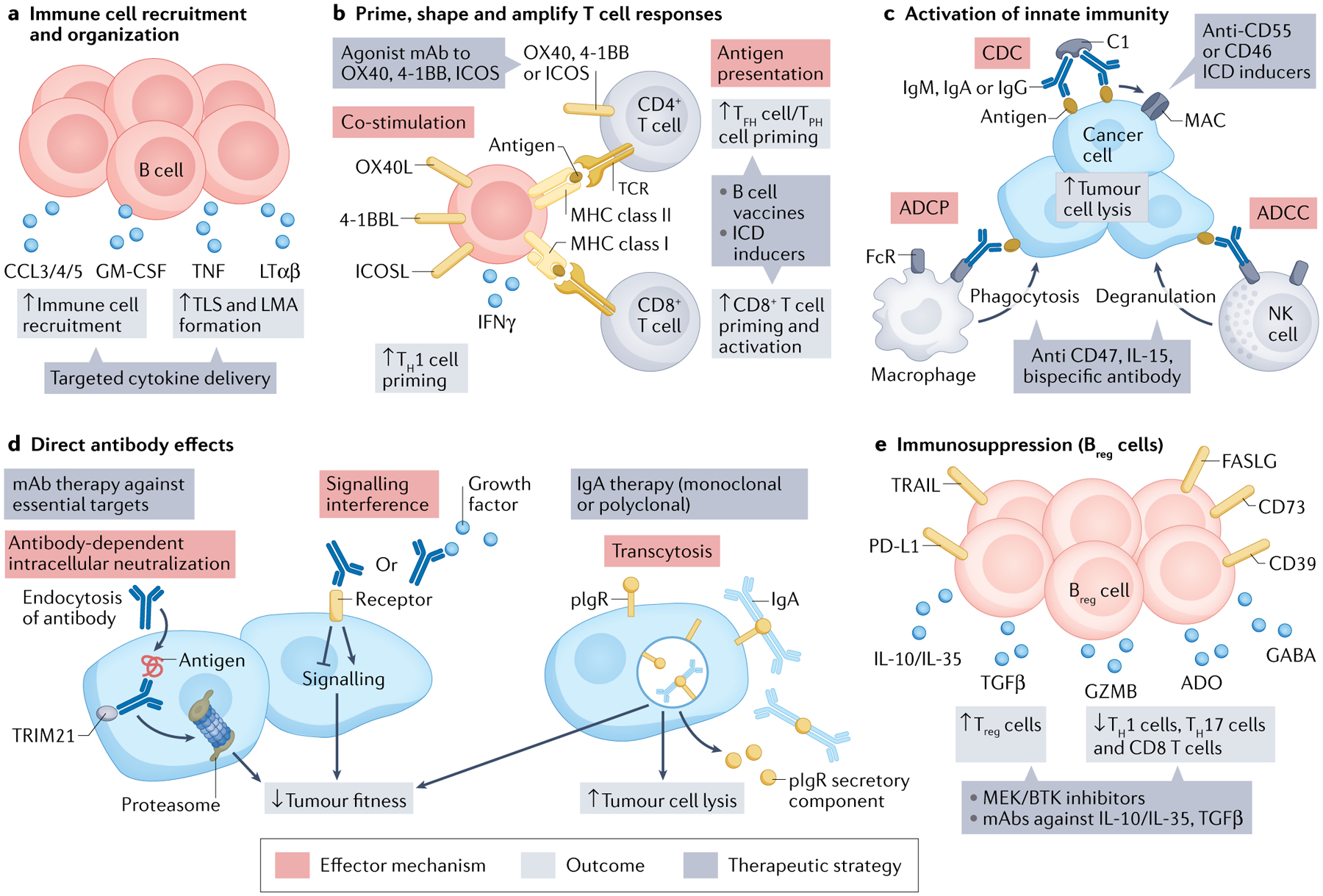
a–e | Five major categories of effector mechanism. ADCC, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; ADCP, antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis; ADO, adenosine; 4–1BBL, 4–1BB ligand; CCL, C–C motif chemokine ligand; CDC, complement-dependent cytotoxicity; FASLG, FAS ligand; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; GZMB, granzyme B; ICD, immunogenic cell death; ICOS, inducible T cell co-stimulatory; ICOSL, ICOS ligand; IFNγ, interferon-γ; LMA, lympho-myeloid aggregate; LTαβ, lymphotoxin-αβ; mAb, monoclonal antibody; MAC, membrane attack complex; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; NK cell, natural killer cell; OX40L, OX40 ligand; PD-L1, programmed cell death 1 ligand 1; pIgR, polymeric immunoglobulin receptor; TCR, T cell receptor; TFH cell, T follicular helper cell; TGFβ, tumour growth factor-β; TH1 cell, T helper 1 cell; TIL-B, tumour-infiltrating B lymphocyte; TLS, tertiary lymphoid structure; TNF, tumour necrosis factor; TPH cell, T peripheral helper cell; TRAIL (or TNFSF10), TNF superfamily member 10; Treg cell, regulatory T cell; TRIM21, tripartite motif containing 21.
