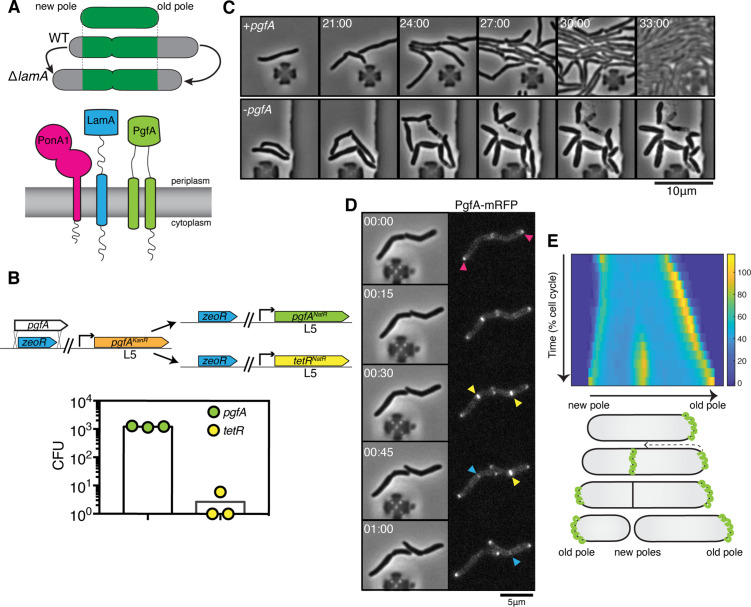
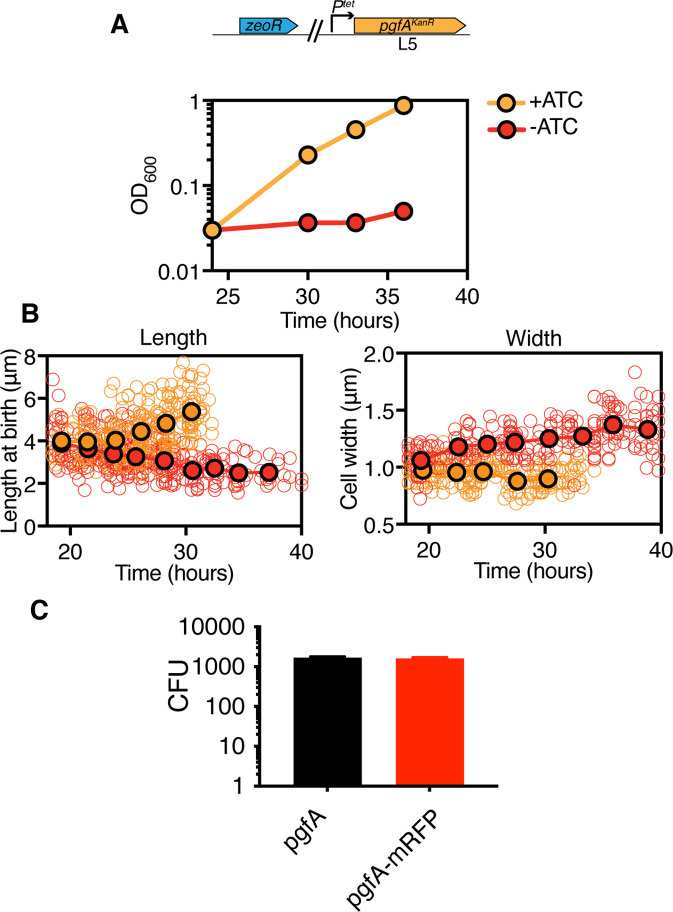
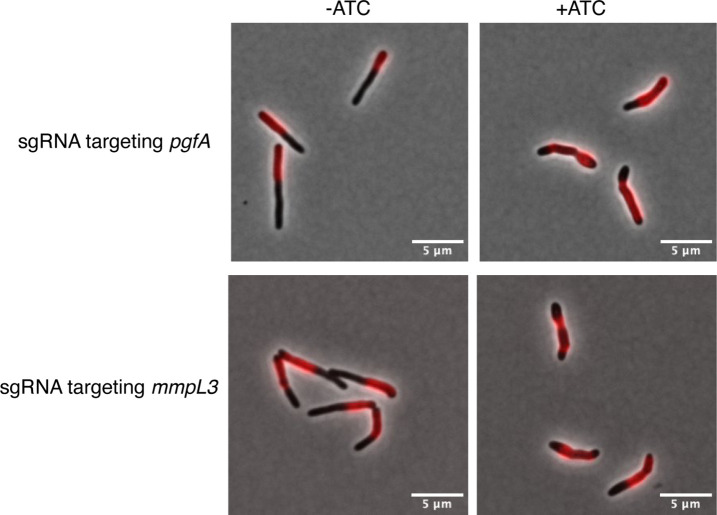
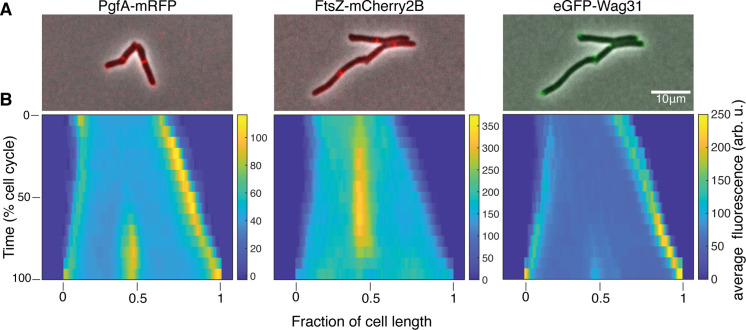
Figure 1. PgfA is an essential polar growth factor that localizes asymmetrically.
(A) Top: Graphical depiction of growth pattern in wild type (WT) and ΔlamA cells. Green = old cell wall material. Gray = new cell wall material. Bottom: LamA is a membrane protein that co-immunoprecipitates with PonA1, a bifunctional penicillin binding protein, and MSMEG_0317/PgfA, a protein of unknown function. (B) Schematic and results of allelic exchange experiment. Vectors with pgfA or without pgfA (tetR) were transformed into a strain whose only copy of pgfA was at the L5 integration site. Transformants carrying the incoming vectors were counted by colony forming units (CFU). (C) A strain whose only copy of PgfA is tetracycline inducible was imaged over time with (+pgfA) or without (-pgfA) anhydrotetracycline (ATC). Cells were loaded into a microfluidic device 18 hr after the removal of ATC (bottom) or a mock control (top). (D) Cells whose only copy of PgfA was fused to mRFP were imaged over time by phase and fluorescence microscopy in a microfluidic device with constant perfusion of media. (E) Top: Individual cells (N=25) were followed from birth to division and the fluorescence was measured from new to old pole. Each resulting kymograph was interpolated over cell length and time and then averaged together. Using this analysis, we find that PgfA is first at the old poles (pink triangles), partially re-localizes to the septum (yellow triangles) during cell division, and then disappears from the site of division before the next cell cycle (blue triangles) to establish asymmetry in the next generation. Bottom: A depiction of this localization pattern is shown as a cartoon.