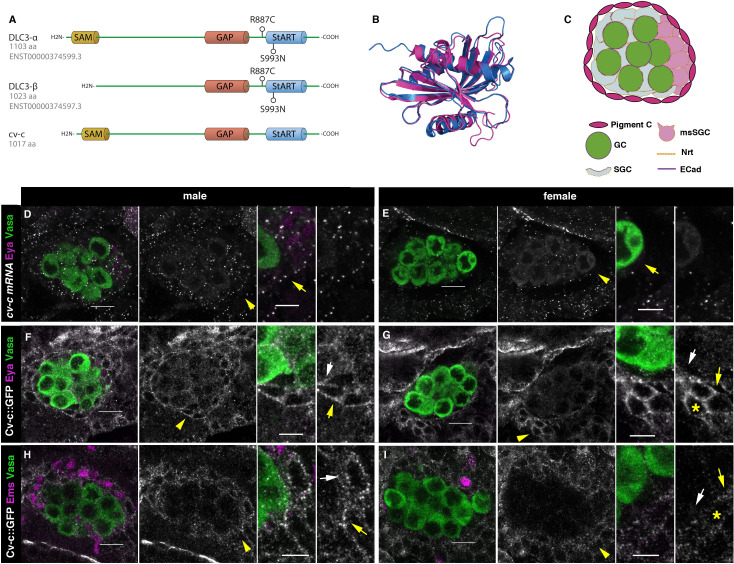
Figure 2. Cv-c and DLC3 structure and cv-c expression in the Drosophila gonad mesoderm.
(A) Linear representation of the DLC3-α, DLC3-β, and Cv-c proteins. The SAM domain is represented in yellow, the GAP domain in orange, and the StART domain in blue. (B) Alignment of the DLC3 (blue) and Cv-c (magenta) StART domains. (C) Schematic representation of the cell types in a Drosophila testis at st17. Germ cells, green; pigment cells, magenta; somatic gonadal cells, grey; male-specific somatic gonadal cells, pink. RNA in situ hybridization of male (D) and female (E) st17 embryos shows general transcription of cv-c in the mesoderm. The right panels in D–I are close ups of the arrowed region in the central panels. (D) In the testis, comparable levels of mRNA puncta can be detected in the somatic mesoderm and in the gonadal mesoderm cells surrounding the male germ cells as are clearly observed in the male-specific somatic gonad precursors (msSGPs) marked by Eya (magenta, indicated by an arrowhead in grey panels and an arrow in the close up). (E) In the ovary, marginal levels of cv-c mRNA expression are observed in the gonadal mesodermal cells, creating a halo of decreased number of puncta surrounding the female germ cells contrasting with the cv-c expressing adjacent somatic mesodermal cells (arrow in close up). (F–I) Cv-c::GFP protein expression in male and female embryos. (F, H) In the testis Cv-c::GFP is detected in the gonadal mesoderm surrounding the germ cells including the male msSGPs (Eya, magenta F) and the pigment cell precursors (Ems, magenta H). (G, I) In females, no substantial GFP signal is detected in the gonadal mesoderm surrounding the germ cells. Note in (F, H) that Cv-c::GFP signal in the gonad mesoderm cells allows tracing the testis contour, while in ovaries (G, I) this is not possible. Higher levels of Cv-c::GFP are present in the ectodermally derived trachea and hindgut. In close ups white arrows point to membranes close to the germ cells, yellow arrows to the membrane of gonad mesodermal cells. In males, Cv-c::GFP can be detected in the membranes between gonadal and somatic mesodermal cells (F, H) whilst in females GFP can only be detected outside the ovary in the membrane of the somatic mesoderm (G, I asterisks). Scale bar: 10 and 5 µm in close ups.