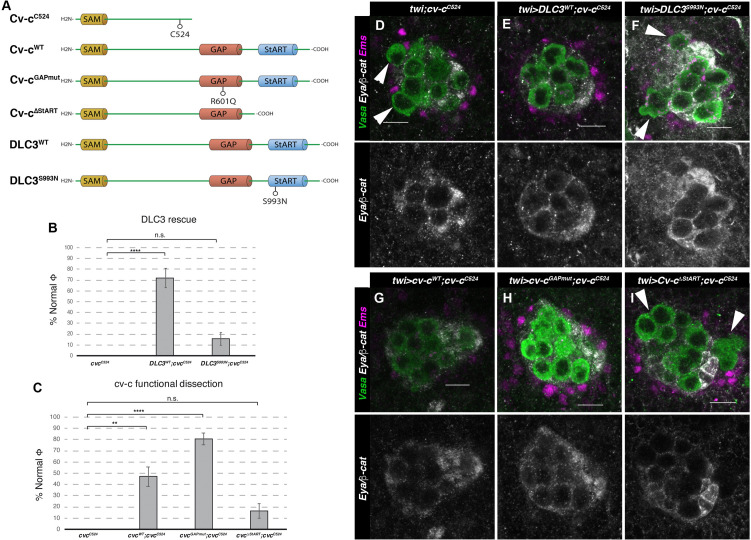
Figure 4. Rescue of cv-c mutant testes.
(A) Schematic representation of Cv-c and DLC3 protein variants studied. Rescue of the dysgenic testis of cv-cC524 homozygous mutant males after expressing the specified (B) DLC3 or (C) Cv-c protein variants under UAS control with the pan mesodermal twi-Gal4 line. Phenotypic rescue is shown as percentage of testes where all germ cells are encapsulated inside the testis. Representative images of testes in (D) control homozygous cv-cC524 animals, or homozygous cv-cC524 animals expressing in the mesoderm either (E) UAS-DLC3WT, (F) UAS-DLC3S993N, (G) UAS-Cv-cWT, (H) UAS-Cv-cGAPmut, or (I) UAS-Cv-cΔStART. Arrows in D, F, I point to extruded germ cells that are not surrounded by β-catenin. Testes are stained with anti-Vasa to label the germ cells (green), anti-Ems to label the pigment cells (purple), and anti-Eya and anti-β-catenin to label the male-specific somatic gonad precursors (msSGPs) and the membranes ensheathing the germ cells, respectively (grey in lower panels). Scale bar: 10 µm. Fisher test, Cv-cWT p = 0.0017 (N = 34), Cv-cGAPmut p < 0.0001 (N = 56), DLC3WT p < 0.0001 (N = 28), Cv-cΔStART p = 0.3005 (N = 31), and DLC3S993N p = 0.3180 (N = 38) (ns, p > 0.05; **p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001) (Figure 4—source data 1).