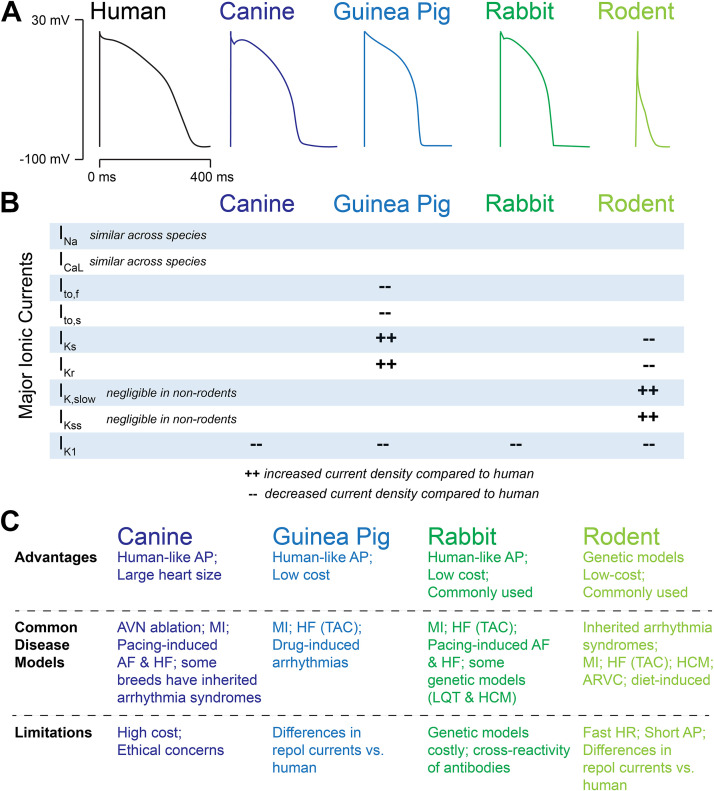
Figure 2.
A: schematic showing approximate ventricular action potential shapes/durations between species. B: major differences in underlying ionic currents compared with the human action potential (AP). C: brief list of advantages, commonly used disease models, and limitations for each species. AF, atrial fibrillation; ARVC, arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy; AVN, atrioventricular node; HCM, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; HF, heart failure; HR, heart rate; LQT, long QT syndrome; MI, myocardial infarction; TAC, transverse aortic constriction. Partially adapted and redrawn from Refs. 20 and 56 with permission.