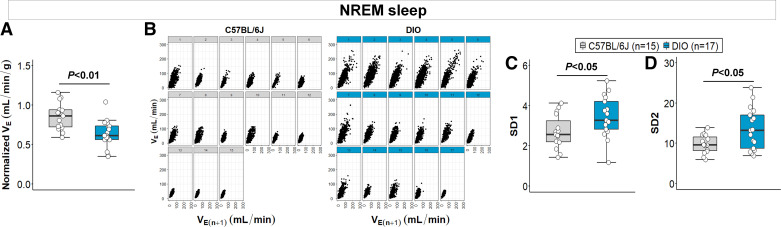
Figure 5.
Obesity is associated with decreased ventilation and augmented breathing variability during NREM sleep. A: normalized minute ventilation (VE) was significantly lower in diet-induced obesity (DIO) mice. B: individual Poincaré plots showed a larger dispersion of VE data points parallel and perpendicular to the line of identity in diet-induced obesity (DIO) mice compared with lean mice. DIO mice showed an augmented short-term and long-term breathing variability during NREM sleep, indicated by higher SD1 (C) and SD2 (D) values, respectively. Median ± 1.5 × IQR are shown (Reprinted from Kim et al. (20) with permission of John Wiley and Sons).