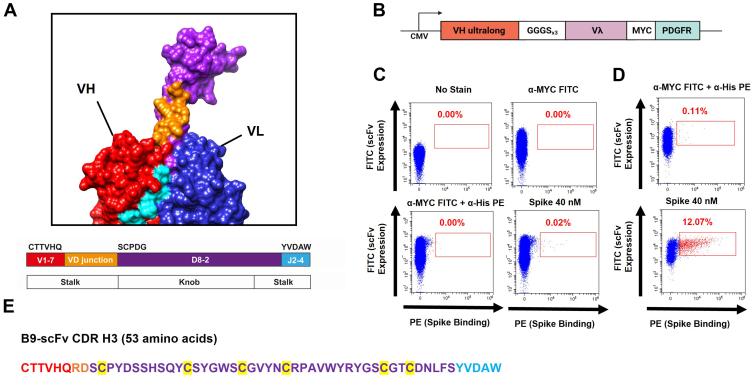
Figure 1.
Cell display and binding of ultralong scFvs to SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein.A, structure of an ultralong CDRH3 stalk and knob domain (PDB: 4K3D) color coded to show the parts encoded by the VH1-7, DH8-2, and JH2-4 gene segments. B, construct used to express membrane-bound scFvs with an ultralong VH under the control of the cytomegalovirus promoter (CMV). The C-terminal Myc tag and platelet-derived growth factor receptor transmembrane domain (PDGFR; for cell surface expression) are shown. C, 293T cells were transfected with round 0 scFv library. Upper: FACS plots of these cells without (left) and with (right) incubation with α-Myc-FITC. Lower: FACS plots showing α-His-PE and α-Myc-FITC staining in the absence (left) or presence (right) of 40 nM Spike. The red box indicates cells expressing scFvs that bind Spike. D, enrichment of Spike-binding scFvs after two rounds of plasmid-based selection. 293T cells were transfected with round 2 plasmid library incubated without (upper) and with (lower) 40 nM Spike. The red box shows cells expressing scFvs that bind Spike. E, the amino acid sequence of the Spike-binding B9-scFv. The regions encoded by V1-7 (blue), the VD junction (orange), D8-2 (dark gray), and J2-4 (green) are shown. Cysteine residues are highlighted in yellow. FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting.