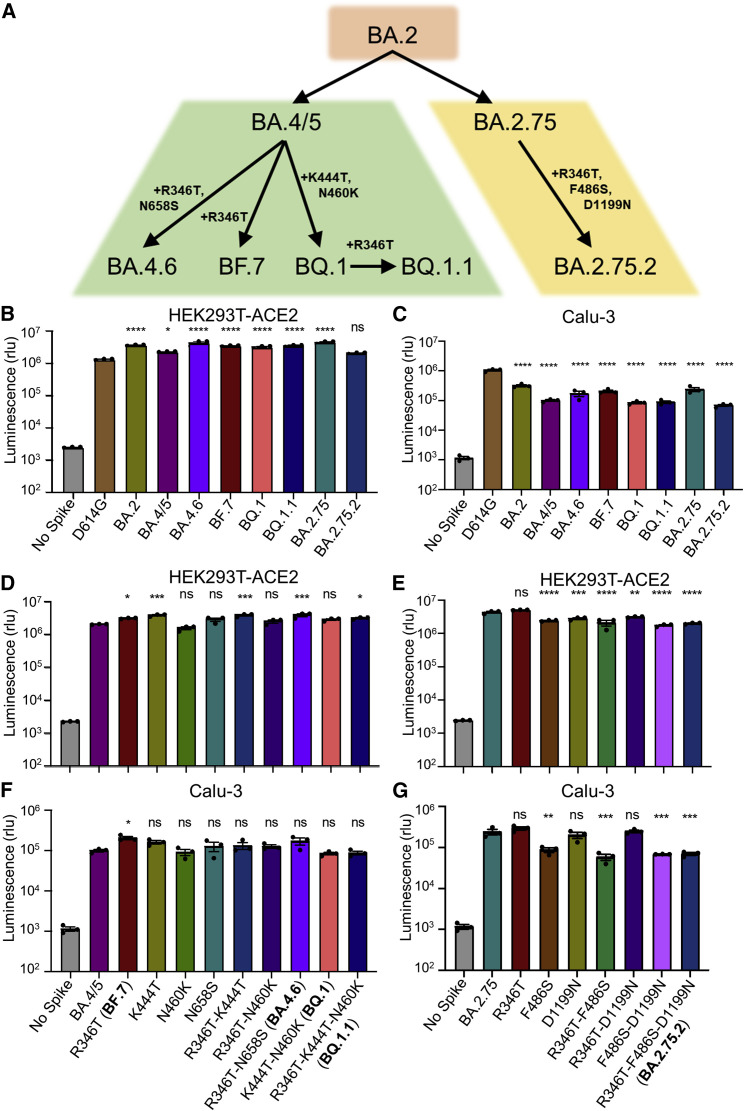
Figure 1.
Omicron subvariant-defining mutations and their impacts on pseudotyped viral infectivity in HEK293T-ACE2 and Calu-3 cells
(A) Displayed is a schematic of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariant evolution indicating the mutations acquired by the BA.4.6, BF.7, BQ.1, BQ.1.1, and BA.2.75.2 subvariants.
(B and C) Infectivity of lentivirus pseudotyped with the indicated Omicron subvariant S constructs in HEK293T-ACE2 cells (B) (n = 3) or in Calu-3 cells (C) (n = 3). Bars represent means ± standard error. Significance relative to D614G was determined by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple testing correction. p values are represented as ns for p ≥ 0.05, ∗p < 0.05, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
(D–G) Infectivity of lentivirus pseudotyped with the indicated BA.4/5-derived mutant S constructs (D and F) (n = 3) or BA.2.75-derived mutant S constructs (E and G) (n = 3) in HEK293T-ACE2 or Calu-3 cells. Bars represent means ± standard error. Significance relative to BA.4/5 or BA.2.75 was determined by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple testing correction. p values are represented as ns for p ≥ 0.05, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.