Fig. 5. Impact of TGF-β signaling on C2C12 myoblast differentiation.
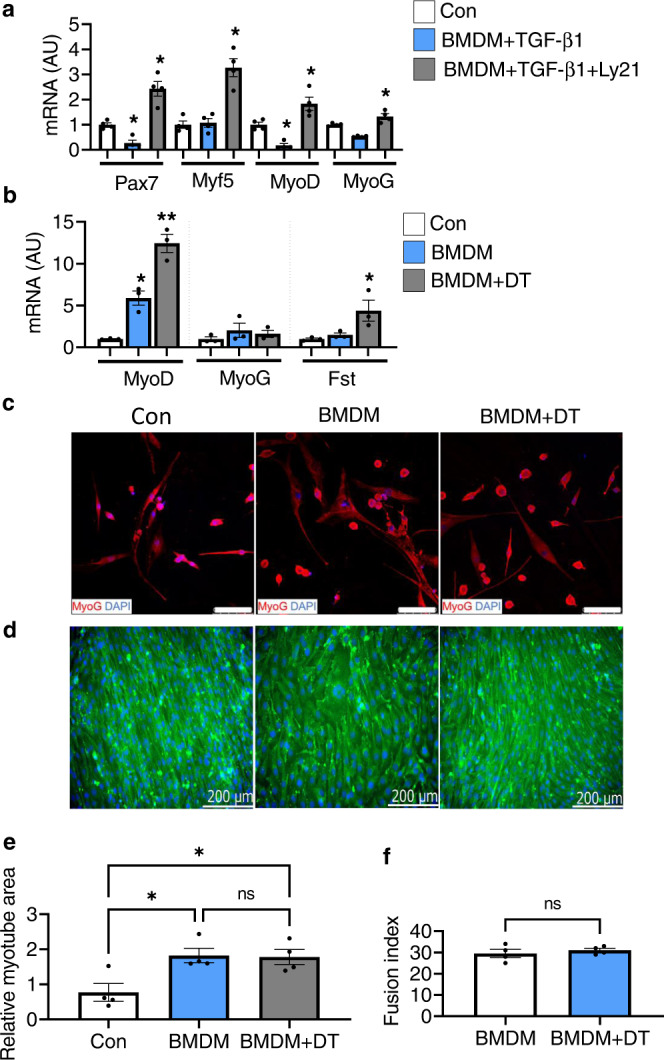
a Relative mRNA expression levels of myogenesis-related marker genes in C2C12 myoblast co-cultured with M2-induced BMDM treated with recombinant TGF-β1 and TGF-β receptor I/II inhibitor (Ly21) (n = 4 wells per group). Data are shown as the means ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc tests. *p < 0.05 was considered as significant. b Relative mRNA expression levels of myogenesis-related marker genes. M2-induced BMDM inhibitory effect on primary myoblast differentiation was released by the depletion of CD206+ M2-like MΦ upon diphtheria toxin (DT) treatment to the BMDM obtained from Tg mice (n = 3 wells per group). Data are shown as the means ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc tests. *p < 0.05, and **p < 0.01 were considered as significant. c Representative images of primary myoblast co-cultured with M2-induced BMDM with or without DT, stained with anti-MyoG antibody (n = 3 wells per group). d Representative images of C2C12 myoblast co-cultured with M2-induced BMDM (obtained from uninjured Tg mice) with or without DT, stained with embryonic myosin heavy chain (eMyH3) antibody, and DAPI (n = 4 wells per group). The images were taken using Keyence microscope. Scale bar 200 μm. e, f Relative myotube area and fusion index were quantified (n = 4 wells per group). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance for e was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc tests, and for f was determined using the two-tailed Student t-test (*p < 0.05, and ns non-significant). AU arbitrary units, Con control, BMDM bone marrow-derived macrophages, and Ly21 Ly2109761 (TGF-β receptor I/II inhibitor).
