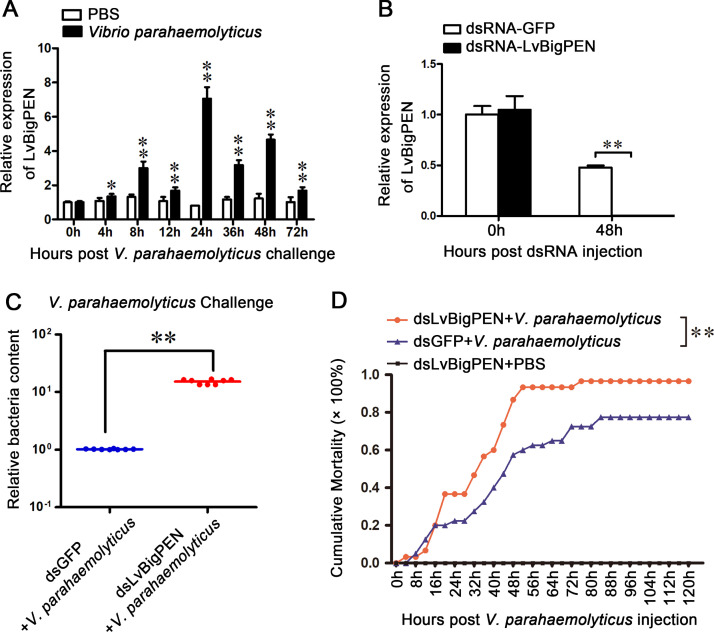
Fig. 2.
Silencing of LvBigPEN during V. parahaemolyticus infected shrimp. (A) Expression profiles of LvBigPEN in hemocytes from V. parahaemolyticus challenged shrimp. Quantitative RT-PCR was performed in triplicate for each sample. The statistical significance was calculated using Student's t-test (**P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05). (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the silencing efficiencies of LvBigPEN in Gills. The internal control was LvEF-1α. Samples were taken at 48 h post-injection and analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR using gene-specific primers for LvBigPEN or GFP. Differences were analyzed using Student's t-test (**P < 0.01). (C) The relative bacterial loads in gills from each group (8 shrimps) were detected by qRT-PCR at 24 h post-infection. Differences between the experimental and control groups were analyzed using Student's t-test (**P < 0.01). (D) Shrimp cumulative mortality following treatment with dsRNAs and infection with V. parahaemolyticus. Cumulative mortality was recorded every 8 h. Differences in cumulative mortality levels between treatments were analyzed by Kaplan–Meier plot (log-rank χ2 test) (**P < 0.01).