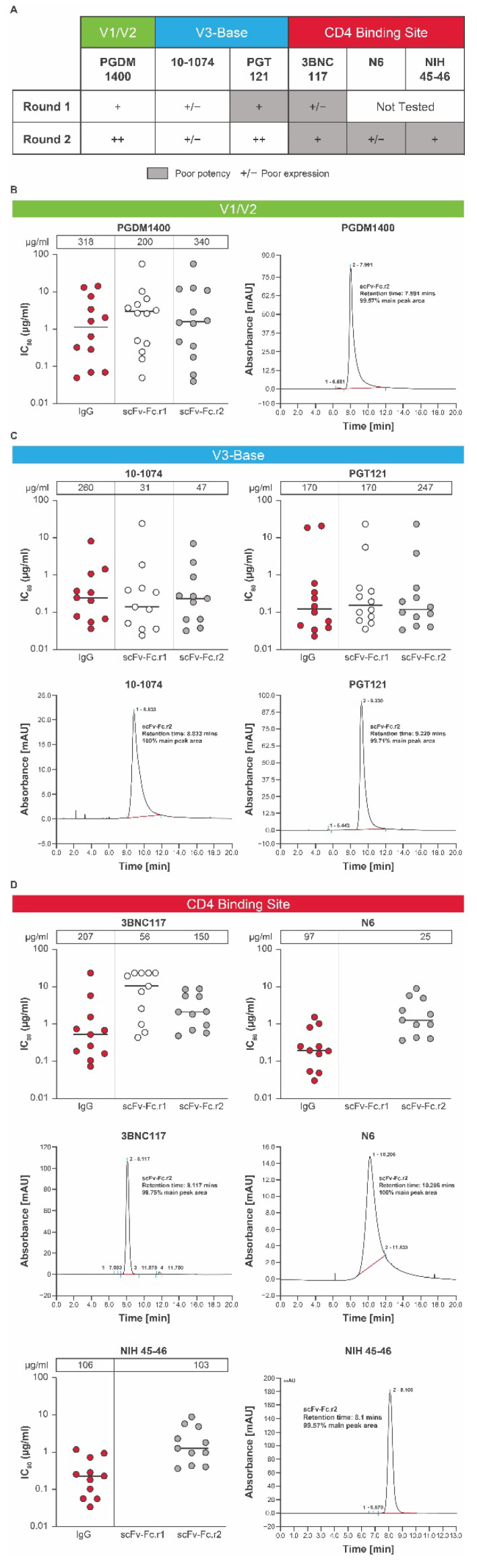
Figure 2.
Conversion into scFv-Fcs of individual HIV bnAbs. (A) A panel of HIV bnAbs (scFv-Fc.r1 and scFv-Fc.r2 designs) targeting 3 key epitopes was tested for in vitro expression and potency. (B) In vitro expression and potency of a PGDM1400 variant with size exclusion chromatography, (C) V3-base variants 10-1074 and PGT121 with size exclusion chromatography, and (D) CD4bs bnAbs 3BNC117, N6, and NIH45-46 over 2 rounds of modifications (round 1 and round 2). In vitro expression concentrations (μg/mL) of the scFv-Fc.r1 and scFv-Fc.r2 designs and their parental IgG antibodies are shown above each figure. Each antibody was tested using a panel of HIV-1 Env pseudoviruses selected based on neutralization sensitivity of the parental bnAb. Protein expression for each mAb and single chain was completed twice. SEC and neutralization analyses were only performed on large scale samples with testing in duplicates each performed once. Note: the lower the IC80, the greater the potency. bnAb, broadly neutralizing antibody; Env, envelope; Fc, crystallizable fragment; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; IC80, inhibitory concentration of 80%; IgG, immunoglobulin G; scFv-Fc, single-chain variable fragment; SEC, size exclusion chromatography.