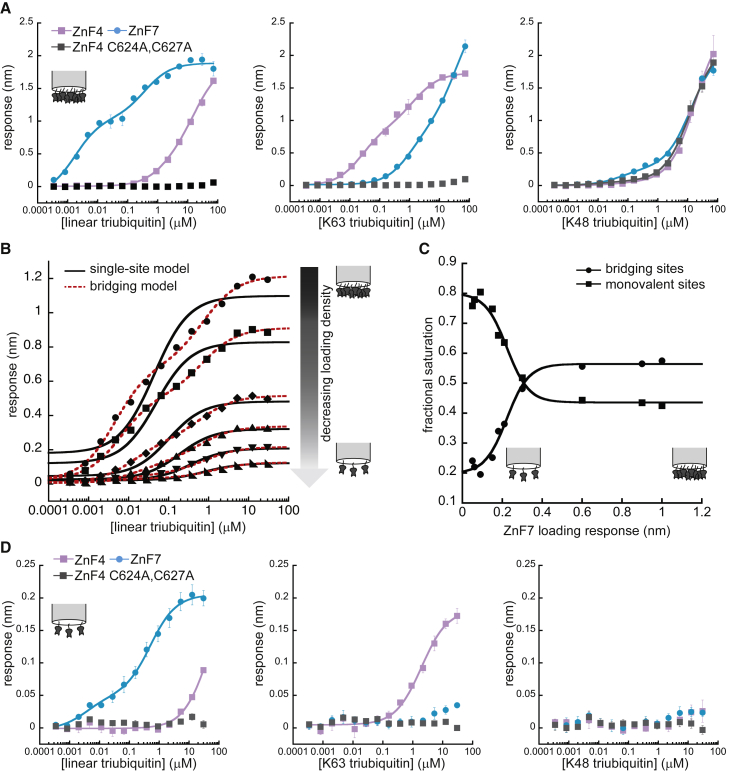
Figure 4.
Ubiquitin binding by A20 ZnF domains. (A) Linear (left), K63-linked (center) and K48-linked (right) triubiquitin binding to monobiotinylated A20 ZnF domains, at ∼1-nm loading response. Data were fit to the bridging model. Error bars indicate the standard deviations from three experiments. (B) Linear triubiquitin-binding ZnF7 at various ZnF7 surface saturation levels: from top to bottom, 1.0-, 0.90-, 0.60-, 0.30-, 0.18-, and 0.090-nm loading response. Fits to single-site binding equation or bridging model shown. (C) Relative bridging (circles) and monovalent (squares) site saturations returned by the bridging model for linear triubiquitin-binding ZnF7 at a range of ZnF7 surface saturation levels. Data fit to a sigmoidal function as a guide to the eye. (D) Linear (left), K63-linked (center) and K48-linked (right) triubiquitin binding to A20 ZnF domains, at ∼0.1-nm loading response. Data are fit to either single-site model (ZnF4) or an independent two-site model (ZnF7) (see Materials and methods), with ZnF4- and ZnF7-binding curves reproduced with permission of Nature (16). Error bars indicate the standard deviations from three experiments. See Figs. S3 and S4 for comprehensive analysis of fitting models with residuals. All fitting parameters from these fits may be found in Tables S1 and S2.