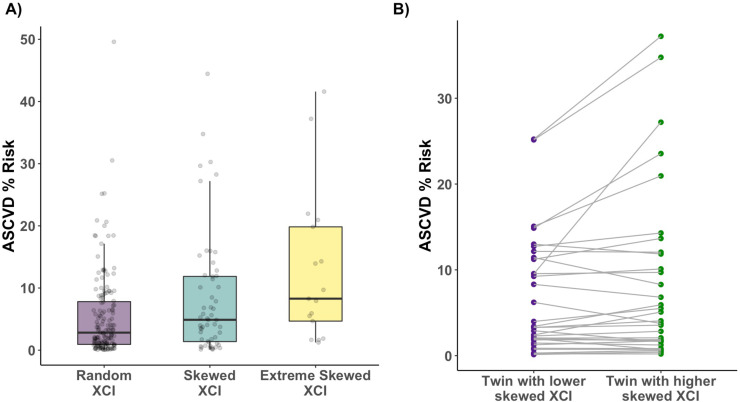
Figure 4. Age acquired XCI-skew and cardiovascular disease risk score.
(A) Using a linear regression mixed effects model to control for BMI, monocyte count, relatedness and zygosity, XCI-skew is associated with increased atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk score (Nranodm XCI = 155; nSkewed XCI = 56; Nextreme skew = 17; p=0.01). The boxplot displays the median and IQR. (B) Using age-matched twin pairs discordant for their XCI-skew status (Npairs = 34), XCI-skew is associated with increased atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk score in the intra-twin analysis (one-sided paired samples Wilcoxon test; p=0.025).