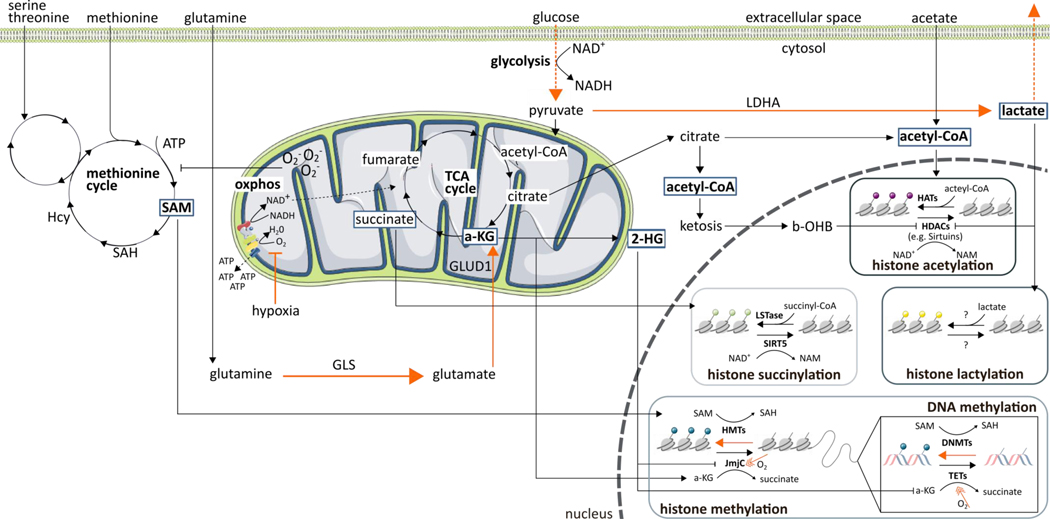
Figure 1. Relationship between immunometabolism, oxygen, and epigenetics.
Numerous metabolic intermediates as well as oxygen availability affect the cellular epigenome. The effects of hypoxia are indicated in orange.
Abbreviations: 2-HG, 2-hydroxyglutarate; a-KG, α-ketoglutarate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate;; b-OHB, β-hydroxybutyric acid; DNMT, DNA methyltransferases; GLS, glutaminase; GLUD1, glutamate dehydrogenase 1; HAT, histone acetyl transferase; Hcy, homocysteine; HDAC, histone deacetylases; HMT, histone methyltransferases; JmjC, Jumonji N/C terminal domains; LDHA, lactate dehydrogenase A; LSTase, lysine succyniltransferase; NAD+/NADH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NAM, nicotinamide; O2-, superoxide; oxphos, oxidative phosphorylation; SAH, S-adenosylhomocysteine; SAM, S-adenosyl-methionine; SIRT, sirtuin; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; TET, ten-eleven translocation methylcytosine dioxygenases