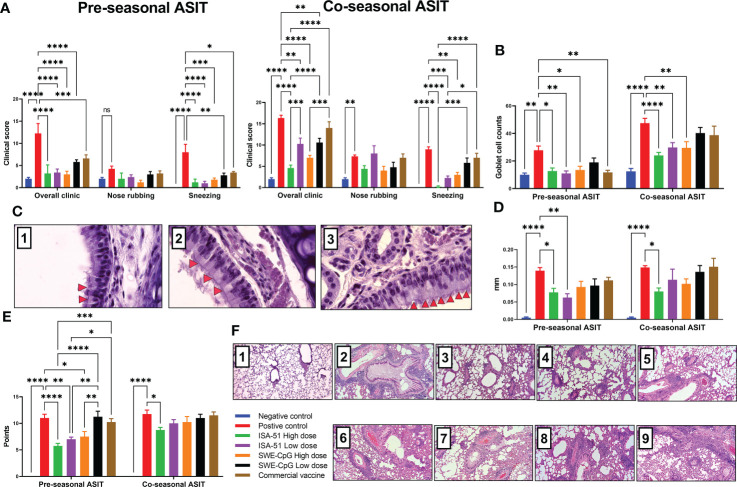
Figure 5.
Therapy for Artemisia vulgaris-induced allergic rhinitis (A–C) and bronchial asthma (D–F) in pre- and co-seasonal ASIT regimen with different vaccine formulations. Allergic rhinitis in mice after challenge with Artemisia vulgaris pollen was evaluated by the intensity of such clinical signs as sneezing, nasal rubbing, and their combination (A), and the number of Goblet cells in nasal mucosal epithelium by histological analysis (B). (C) - histology of mouse nasal turbinates (Hematoxylin-Eosin staining; x1000): 1. Negative control, 2. ASIT group, 3. Positive controls. Red arrows indicate hyperplasia of the Goblet cells. The effectiveness of bronchial asthma therapy after ASIT was based on the results of the ear swelling test (D) and the level of lung pathological changes of mice (E) after challenge. The results of the ear swelling test are presented as the delta in the thickness of mouse auricles with the allergen or PBS, which was expressed in mm. Lung histological analysis after challenge was performed on a 16-point score (non-Type 2 inflammation). (F) - overview lung pictures of mice in different groups, x100 magnification: 1. Negative control; 2, 6. Positive controls in the pre- and co-seasonal ASIT regimens, respectively; 3, 7. ISA-51 groups in pre- and co-seasonal ASIT regimens, respectively; 4, 8. SWE-CpG groups in pre- and co-seasonal ASIT, respectively; 5, 9. Commercial vaccine group in pre- and co-seasonal ASIT regimens, respectively; Differences in the studied parameters between animal groups were assessed using Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. NS - not significant. A P<0.05 value was considered a significant difference. *P <0.05, **P <0.01, ***P <0.001, and ****P <0.0001.