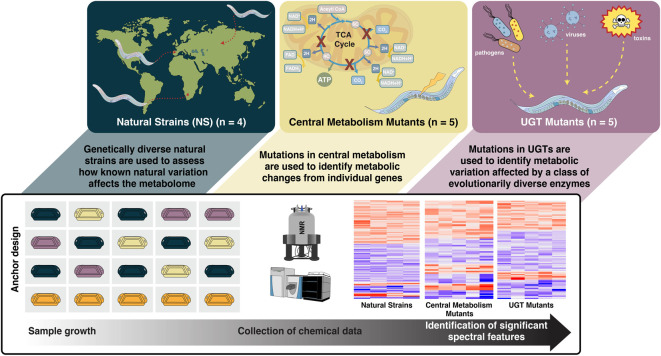
FIGURE 1.
Fourteen C. elegans strains are evaluated in three genetic studies (natural strains, central metabolism mutants, and UDP- glucuronosyltransferase mutants). PD1074, the anchor control strain (orange), is grown alongside test strains (green, yellow, purple). Multiple biological replicates of PD1074 capture environmental variation in growth conditions. Non-polar and polar metabolic data were collected by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Data acquisition controls included biological reference material, pooled PD1074, pooled test strains, and extraction blanks. Biological replicates of PD1074 (n = 42 for LC-MS, n = 52 for NMR) were assayed individually and allocated across all data acquisition batches. Meta-analysis between PD1074 and individual test strains provided comparable inferences to mixed effects models, and the resulting estimated relative effects of each test strain to PD1074 provide straightforward comparisons of test strains between studies.