Figure 1.
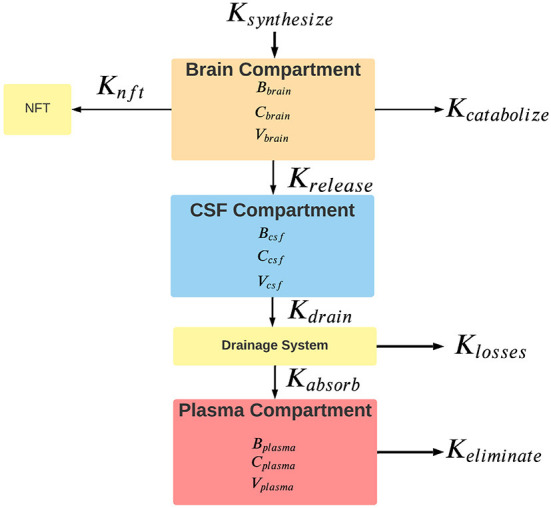
Rates of the flow of tau between model compartments. For each compartment, B is the total tau in pg, C is the tau concentration in pg/ml, and V is the compartment volume in ml. Rates are shown with a capital K and are nominally expressed in units of pg/hr. Ksynthesize is the synthesis rate of tau, Kcatabolize is the internal rate of tau catabolism (destruction) within neurons. Krelease is the rate of tau release from neurons into the interstitial fluid. Some cytosolic tau is converted to neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) in the neuron at an unknown rate of Knft. Clearance of tau from the brain compartment is the sum of rates of catabolism, release, and conversion to neurofibrillary tangles. Kdrain is the rate that tau enters the drainage system. The tau drainage system from the CSF likely encompasses a variety of mechanisms, including the arachnoid granulations of the CSF, the glymphatic system, connections between the CSF and olfactory and meningeal lymphatics, and the periarterial drainage system. Clearance of tau from the CSF reflects the contributions of all of these drainage systems to removing tau from the CSF. Klosses is the rate of loss of tau in the drainage system. Kabsorb is the tau absorption rate into the plasma compartment. Keliminate is the rate that tau is eliminated from the plasma compartment. Elimination from the plasma occurs through various mechanisms, including renal excretion, hepatic metabolism, and intravascular proteolysis. Clearance from the plasma reflects all of these elimination mechanisms.
