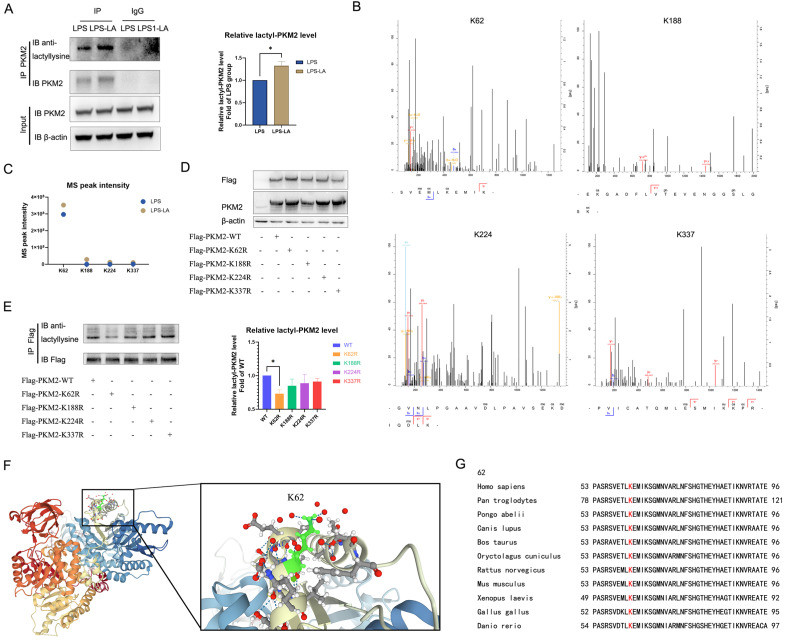
Figure 5.
Lactate promotes K62 lactylation of PKM2. (A) Naïve bone-marrow-derived macrophage cells were incubated with 100 ng/ml lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 4 hr, followed by vehicle (LPS) or 20 mM lactate (LPS+LA) for 20 hr. Then cell proteins were pulled down by PKM2 antibody and detected with anti-lactyllysine antibody. (B) We detected possible lactylation sites of PKM2 in LPS-induced BMDM cells through immunoprecipitation (IP)-mass spectrometry analysis. The four possible lactylation sites of PKM2 through IP-mass spectrometry are shown. (C) The observed mass spectrum peak intensity of lactyl-lysine-containing peptides in BMDM cells (incubated with 20 mM lactate or not). (D) K62R, K188R, K224R, and K337R site mutations, or wild-type flag-PKM2 overexpressed 293T cells were constructed respectively through overexpression plasmid. Cell proteins were analyzed by western blotting (WB) for PKM2 levels. (E) Flag-PKM2 overexpressed 293T cells proteins were pulled down by flag antibody and detected with anti-lactyllysine antibody. (F) Ribbon diagram of the crystal structure of human PKM2 protein (PDB entry 6B6U). (G) The K62 site in PKM2 is conserved. The sequences around PKM2 K62 from different species were aligned. Conserved lysine residues corresponding to human PKM2 K62 are marked in red. WB data represents three independent experiments. Data represents mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05.