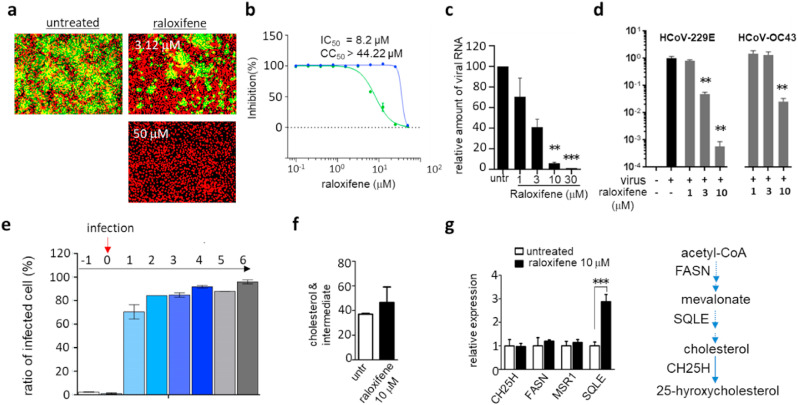
Fig. 5.
Raloxifene inhibits the early stage of coronavirus infection. a) Antiviral activity of raloxifene demonstrated by an immunofluorescence-based MERS-CoV infection assay as previously noted in Fig. 4a. Green signals represent cells infected with MERS-CoV and red signals represent cell survival. b) In total, ten different concentrations of raloxifene were tested in the immunofluorescence assay, and EC50 and cytotoxicity were calculated through curve fitting analysis using Prism 6. c) Viral mRNA quantified by qRT-PCR from the Vero cells infected with MERS-CoV. d) Potency of raloxifene against HCoV-229E or HCoV-OC43 measured by qRT-PCR as detailed in Fig. 4d. e) Time-of-addition experiment using 10 μM of raloxifene. Experiments were performed as described in Fig. 4c. f) Cellular cholesterol levels in A549 cells treated with 10 μM raloxifene for 12 h. g) Expression levels of selected genes involved in cholesterol metabolism quantified by qRT-PCR after 12 h of treatment with 10 μM raloxifene. CH25H; cholesterol 25-Hydroxylase, FASN; fatty acid synthase, MSR1; macrophage scavenger receptor 1, SQLE; squalene epoxidase. Each data point represents the mean ± SEM of triplicate assays.