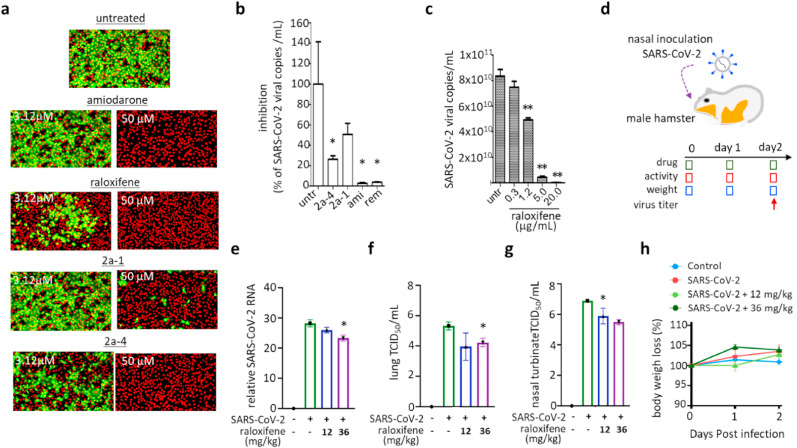
Fig. 7.
Compounds inhibiting the early stage of coronavirus infection show potency against both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 infection. a) Antiviral activity of the selected broad-spectrum compounds (amiodarone, raloxifene, 2a-1, and 2a-4) demonstrated by immunofluorescence-based SARS-CoV infection assay. Among the ten different concentrations (1–50 μM) of each compound examined, images at low (3.12 μM) and high (50 μM) concentrations were selected. Green signals represent cells infected with SARS-CoV and red signals represent cell survival. b-c) Potency of the selected drugs against SARS-CoV2 infection demonstrated with a cell-based infection model. Cells were treated with 10 μM of amiodarone, 2a-1, and 2a-4 (b), raloxifene (c) at the time of infection with SARS-CoV-2, and viral mRNA was quantified by qRT-PCR after 24 h of infection. For comparison, 10 μM of remdesivir was included. d-g) In vivo potency of raloxifene against SARS-CoV-2 demonstrated using a hamster infection model. d) Schematic presentation of SARS-CoV2 infection and sampling. SARS-CoV-2 was infected through nasal inoculation and animals were treated with raloxifene during a two-day infection period at 12 mg/kg or 36 mg/kg doses. On day 2, viral titer in the hamsters was measured by qRT-PCR. e-f) Viral titers of SARS-CoV-2 in lungs quantified on day 2 by qRT-PCR (e) or TCID50 (f). g) Viral titer of nasal turbinate quantified on day 2 by TCID50. h) Body weight of the hamsters was measured daily for the 2-day infection period and they remained normal. Each data point represents the mean ± SEM of triplicate assays.