Figure 1.
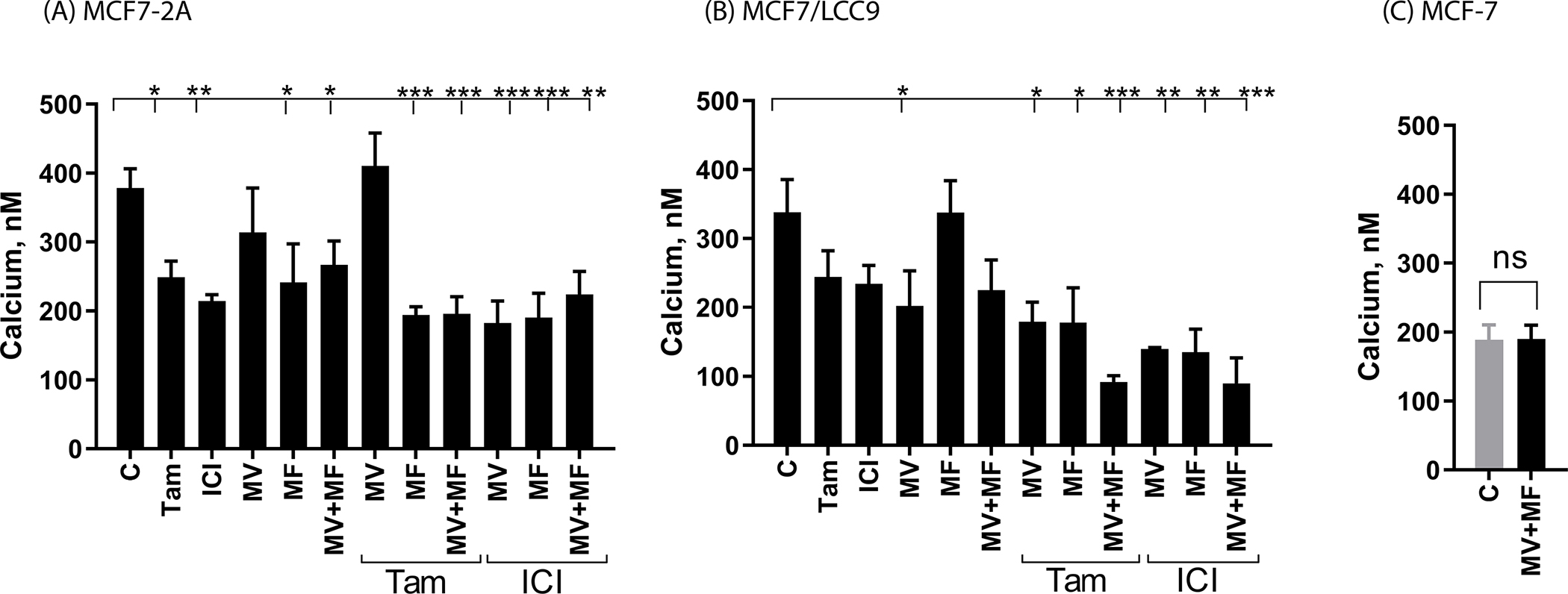
Effects of calcium channel blockers on the concentration of intracellular calcium
MCF7-2A and MCF7/LCC9 cells were grown in phenol red free IMEM supplemented with 5% CFBS. MCF-7 cells were grown in phenol red containing IMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum; prior to treatment, the media of MCF-7 cells was changed to phenol red free IMEM containing 5% CCS for 48 hours. Cells were treated for 72 hours with methoxyverapamil (MV; 75 μM) and/or mibefradil (MF; 5 μM) in the absence and presence of 17β-estradiol (E2; 1 nM), 4-hydroxy tamoxifen (TAM; 1 μM), or ICI-182,780 (ICI; 100 nM). To quantify the concentration of intracellular calcium, the cells were trypsinized and incubated for 20 minutes with 5 uM Fluo-4-AM. The emission at 516 nm was determined using an excitation wavelength of 494 nm and the concentration of intracellular calcium was calculated using the equation: [Cain 2+] = Kd × ([F − Fmin])/ ([Fmax −F]) where Kd is the affinity of the dye for calcium. Data are the mean ± SEM (n ≥ 3). *, p≤0.05; **, p≤0.01; ***, p≤0.001; ****, p≤0.0001. panel A, MCF7-2A cells; panel B, MCF7/LCC9 cells; panel C, MCF-7 cells.
