Figure 4: Enteric Neuron/Goblet Cell Crosstalk.
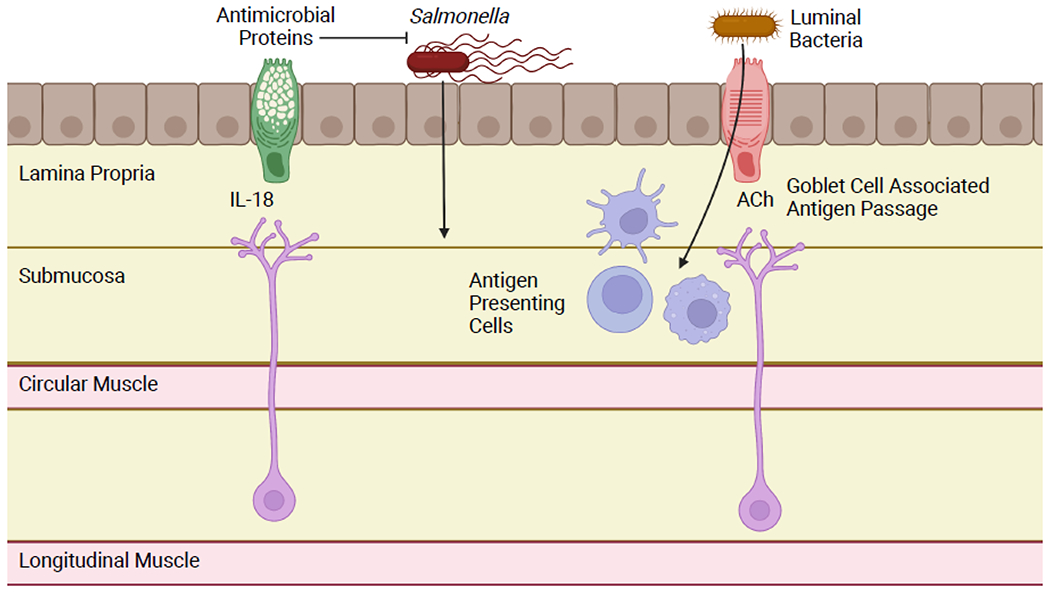
Enteric neurons produce the cytokine IL-18 constitutively. This induces goblet cells to produce antimicrobial proteins under homeostatic conditions and promotes host defense in the context of Salmonella infection. Goblet cells can also form portals, known as goblet cell associated antigen passages (GAPs). GAPs facilitate physiologic and pathologic translocation of luminal bacteria and presentation to antigen presenting cells. Goblet cells are induced to form GAPs by acetylcholine activation of the mAChR4 receptor. Cholinergic enteric neurons have been hypothesized as an important source of acetylcholine for GAP activation. Figure generated using BioRender.com.
