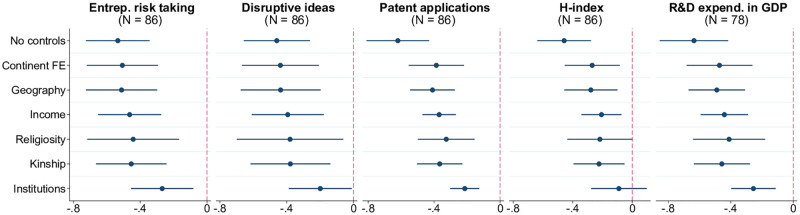
Fig 7. Witchcraft beliefs and innovation.
Each panel of the figure presents the results of estimating 7 different models, in which the metric of innovation indicated in the panel title is regressed on the prevalence of witchcraft beliefs, along with a set of control variables. The latter is defined as follows according to the tickmarks on the vertical axis: 1) none for “No controls”, 2) only continental fixed effects for “Continent FE”, 3) continental fixed effects and baseline geographic controls (absolute latitude, terrain ruggedness, agricultural suitability of land, distance to the coastline) for “Geography.” The remaining 4 models, named “Income,” “Religiosity,” “Kinship,” and “Institutions” include, respectively, real GDP per capita, average religiosity, kinship intensity index, and the rule-of-law index (in addition to continental fixed effects and geographic variables). The round marker represents the point estimate for the coefficient on the prevalence of witchcraft beliefs, and the linear segment around each marker is the respective 95% confidence interval based on heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors. Sample size N indicated in parentheses. The key variables are standardized to have zero mean and unit standard deviation in relevant samples.