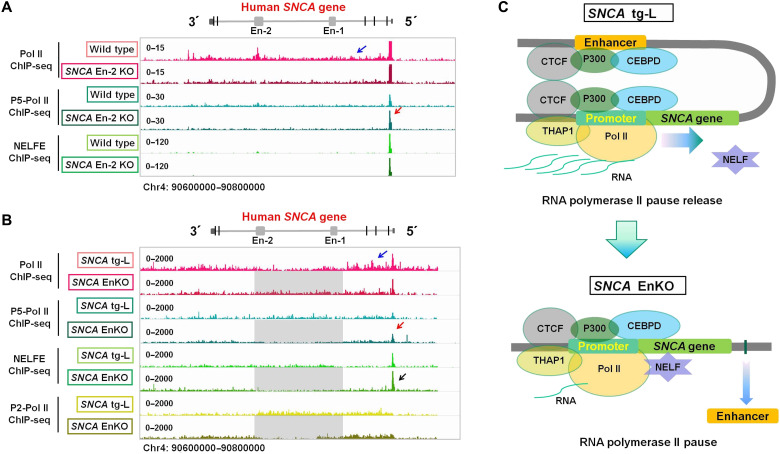
Fig. 7. The human SNCA intronic enhancer clusters promote release of paused RNA Pol II.
(A) ChIP-seqs show the binding profiles of RNA Pol II, serine-5 phosphorylated Pol II (P5-Pol II), and NELFE in wild-type and SNCA En-2 KO SH-SY5Y cells. (B) ChIP-seqs show the binding profiles of Pol II, P5-Pol II, NELFE, and serine-2 phosphorylated Pol II (P2-Pol II) in the SNCA tg-L rat cortex and SNCA EnKO rat cortex. (A and B) The blue arrow indicates Pol II binding signal on the human SNCA gene body. The red arrow shows the increased binding signal of P5-Pol II on the SNCA promoter in SNCA En-2 KO SH-SY5Y cells and SNCA EnKO rat cortex compared to wild-type SH-SY5Y and SNCA tg-L rat cortex, respectively. The black arrow shows that the NELFE binding signal is stronger in the SNCA En KO rat cortex than in the SNCA tg-L cortex. (C) Schematic graphs show the structures and transcription regulators of the human SNCA gene in wild-type (SNCA tg-L) and in enhancer cluster knockout (SNCA EnKO) conditions. The human SNCA promoter was bound by many transcription factors and makes contact with its intronic enhancer (Enhancer). The contact between promoter and enhancer promotes the release of Pol II pause and transcription elongation (top). Knocking out the intronic enhancer clusters (enhancer) of the human SNCA gene loses the contact between enhancer and promoter and increases the enrichment of NELF on its promoter, which causes RNA Pol II pausing (bottom).