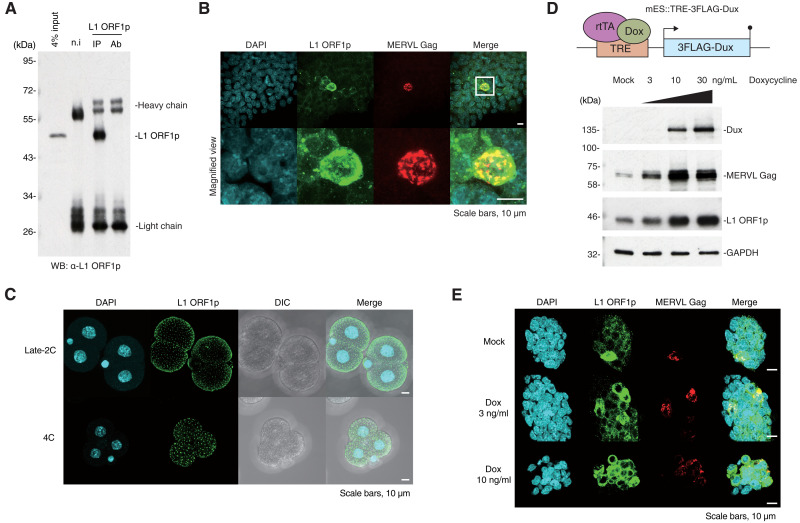
Fig. 1. Characterization of L1 ORF1p in mESCs and mouse preimplantation embryos.
(A) IP of endogenous L1 ORF1p in wild-type mESCs followed by WB. n.i, nonimmunized mouse [immunoglobulin G (IgG) control]; Ab, antibody only. (B) Immunofluorescence of wild-type mESCs shows colocalization of endogenous L1 ORF1p and MERVL Gag in 2C-like cells. Images are maximal Z projections of confocal sections. (C) Immunofluorescence of mouse embryos at late two-cell (2C) stage and four-cell (4C) stage. L1 ORF1p localized on the surface of the embryo with evenly scattered foci. Also see fig. S1B. Images are maximal Z projections of confocal sections. DIC, differential interference contrast microscope. (D) Top: Scheme of mES::TRE-3FLAG-Dux cell line construct. 3FLAG-Dux is inserted after the TRE promoter, which drives downstream gene expression upon induction by doxycycline. Bottom: MERVL Gag and L1 ORF1p are up-regulated in mES::TRE-3FLAG-Dux cell line in a doxycycline dose-dependent manner. (E) Immunofluorescence of mES::TRE-3FLAG-Dux cells. Images are maximal Z projections of confocal sections. Proportion of cells expressing L1 ORF1p and MERVL Gag were increased in a doxycycline dose-dependent manner.