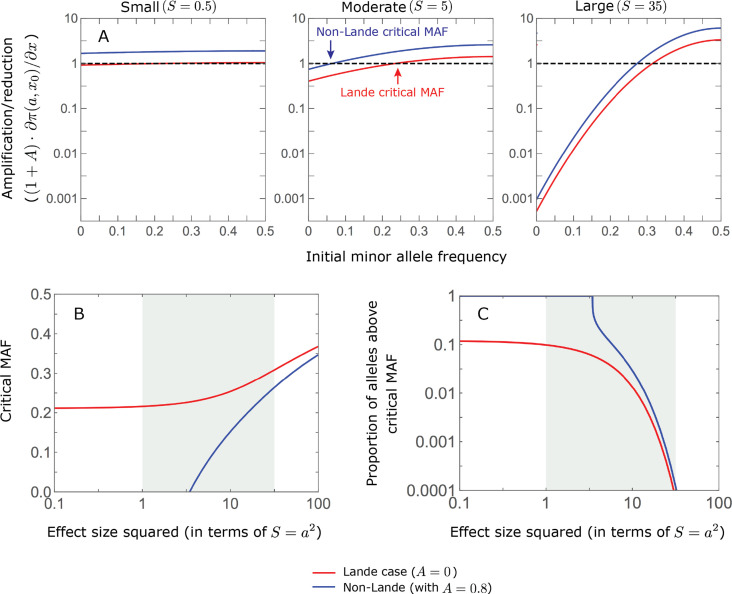
Appendix 2—figure 3. The long-term phenotypic contribution of minor alleles is amplified if they start above a critical initial frequency, which depends on their magnitude, and it is diminished if they start below this critical MAF.
(A) The amplification/reduction for alleles with small (left), moderate (middle), and large (right) effects as a function of initial MAF, in the Lande (red) and non-Lande (blue) case. The curves and critical MAFs are calculated from the above equations. Given a factor , the contribution of alleles with sufficiently small effect sizes are amplified for any initial MAF (Figure 6), because and thus and . In turn, for sufficiently large effect sizes, the curves for and ( ) intersect (Figure 6B) and thus a critical MAF exists (i.e., ). These considerations explain why, for sufficiently large effect sizes, the long-term contribution of alleles with low initial MAFs is diminished relative to their short-term contribution. (B) The critical MAF as a function of effect size in the Lande and non-Lande case (based on ). The critical MAF is lower in the non-Lande case, because . This proportion declined with increasing allele magnitude both because initial MAFs at equilibrium decrease and because the critical MAF increases (panel B). It is greater in the non-Lande case because the critical MAF is lower (panel B). (C) The proportion of segregating sites at equilibrium with MAF exceeding the critical MAF.