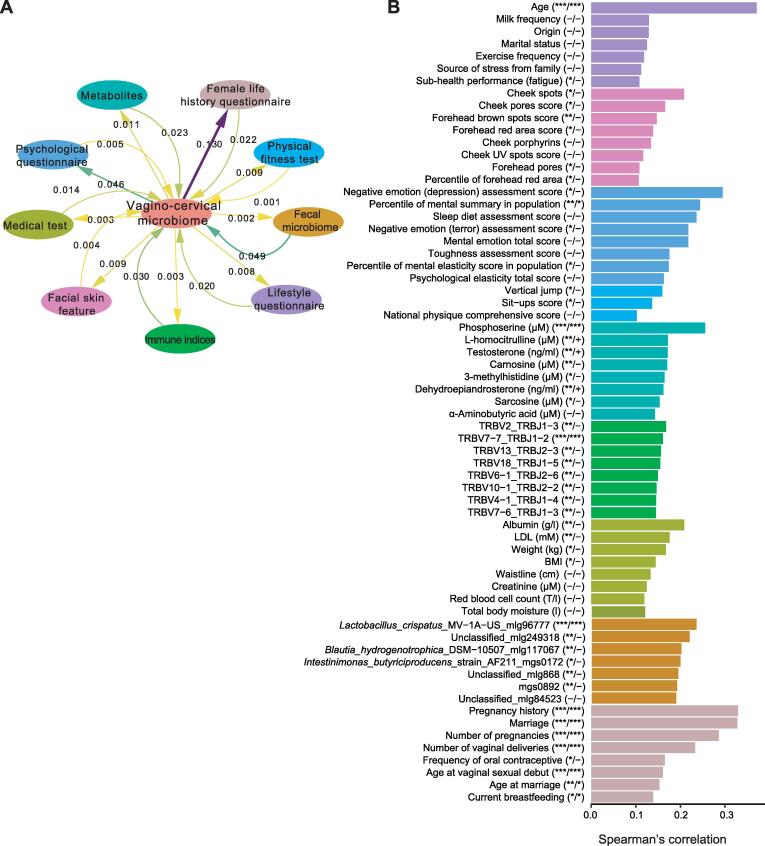
Figure 4.
Global view of factors influencing the vagino-cervical microbiome in the initial study cohort
A. Predicting the vagino-cervical microbiome from each omic dataset and vice versa using stepwise redundancy analysis. Numbers on the straight arrows indicate adjusted R-squared from vagino-cervical microbiome to multi-omic data; numbers on the curved arrows indicate adjusted R-squared from multi-omic data to vagino-cervical microbiome. B. Top 8 factors in each type of multi-omic data that are predicted by the vagino-cervical microbiome. Each covariate from the multi-omic data is detailed in Table S1. X-axis (length of the bar) is the model performance measured as the Spearman’s correlation coefficient between the prediction and measurement. In the parentheses after Y-axis labels, the first column symbols are P values with 999 permutations, and the second column symbols are Q values for BH method (32 comparisons). “−” denotes value ≥ 0.1, “+” denotes 0.05 ≤ value < 0.1, “*” denotes value < 0.05, “**” denotes value < 0.01, and “***” denotes value < 0.001.