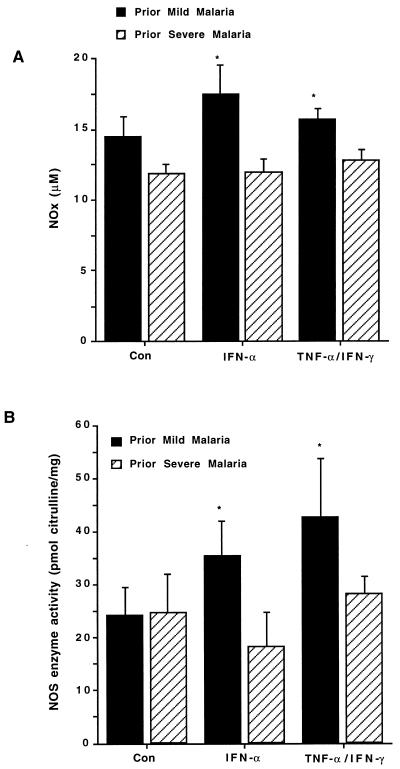
FIG. 1.
NOx and NOS enzyme activity in cultured PBMC. PBMC were prepared from healthy children who previously had mild P. falciparum malaria (n = 18) and from healthy children who previously had severe P. falciparum malaria (n = 10). Cultures were incubated for 7 days with medium alone (controls), INF-α2b (50 U/ml), or TNF-α (10 ng/ml) and IFN-γ (500 U/ml). Culture supernatants were removed and assayed in triplicate for NOx (micromolar). PBMC were harvested, lysates were prepared, and NOS enzyme activity (picomoles of citrulline/milligram of protein) was determined in triplicate by measuring the conversion of l-[14C]arginine to l-[14C]citrulline. The graphs show the means + standard errors of the mean (error bars) for each of the two groups. Comparisons between the PMM and PSM groups were made by using the Wilcoxon rank sum and Mann-Whitney U tests (statistical significance [P < 0.05]). ∗, P < 0.05 (for the PMM versus the PSM groups).