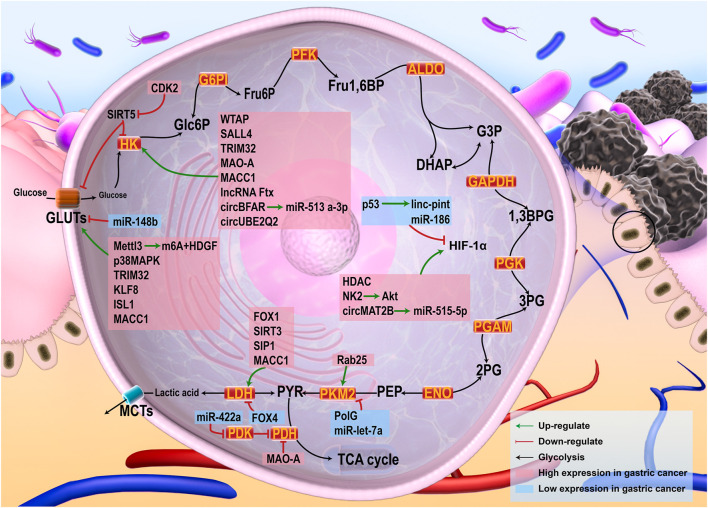
FIGURE 1.
Glycolysis in cancer cells and the related regulatory pathways. Glucose was uptaken into cells by GLUTs, where it is metabolized into pyruvic acid by a series of enzyme reactions. Pyruvic acid could be metabolized by LDH to lactic acid out of the cells, or by PDH to acetyl-CoA into the TCA cycle when oxygen supply is adequate. HIF-1, the main regulator of glycolysis, was able to up-regulate the expression of a variety of enzymes in the glycolysis process. Multiple tumor-related pathways were involved in regulating glycolysis of gastric cancer. Factors with high expression in gastric cancer, such as HDAC and WTAP, can directly promote glycolysis of gastric cancer by up-regulating the expression of glycolysis-related proteins or enzymes. Some factors that can inhibit glycolysis-related enzymes, such as FOX4, miR-186, etc., were low expressed in gastric cancer.