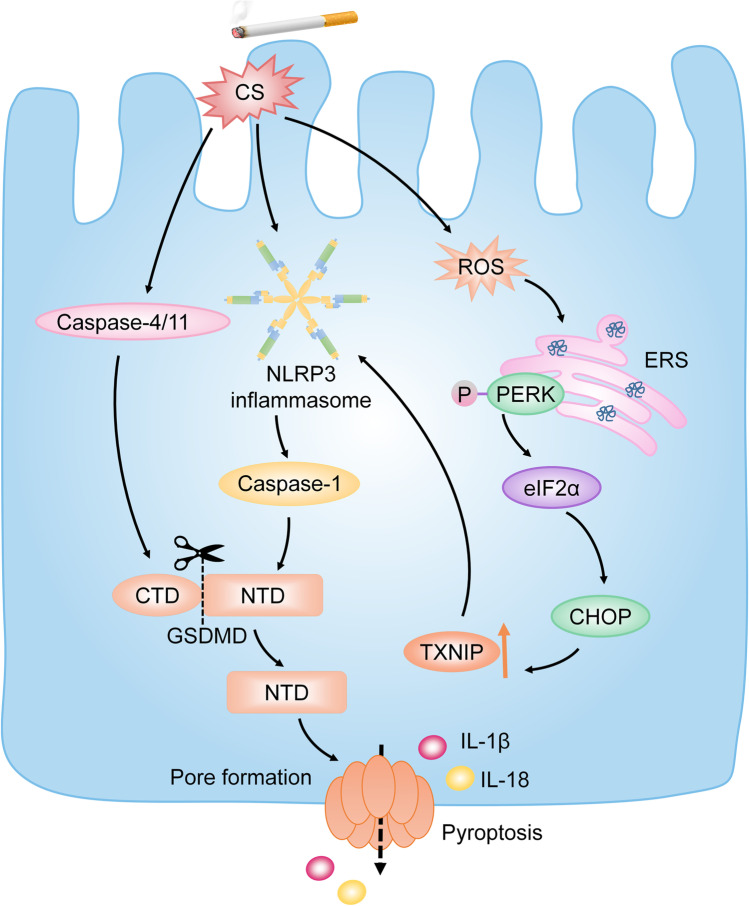
Fig. 4.
Pyroptosis in COPD. CS is the predominant risk factor for COPD. CS triggers pyroptosis of BECs by activating the NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway. Meanwhile, CS induces ERS to trigger pyroptosis of BECs via mediating the generation of sufficient ROS. The initiation of CS-induced ERS results in the activation of PERK, which sequentially upregulates TXNIP by activating the PERK/eIF2α/CHOP pathway. Increased TXNIP contributes to the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Consequently, pyroptosis occurs. Additionally, CS induces caspase-4/11-induced pyroptosis in BECs and accelerates airway remodeling. Note: COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CS, cigarette smoke; BECs, bronchial epithelial cells; ERS, endoplasmic reticulum stress; PERK, protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; TXNIP, thioredoxin interacting protein; eIF2α, eukaryotic translation-initiation factor 2α; CHOP, CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein