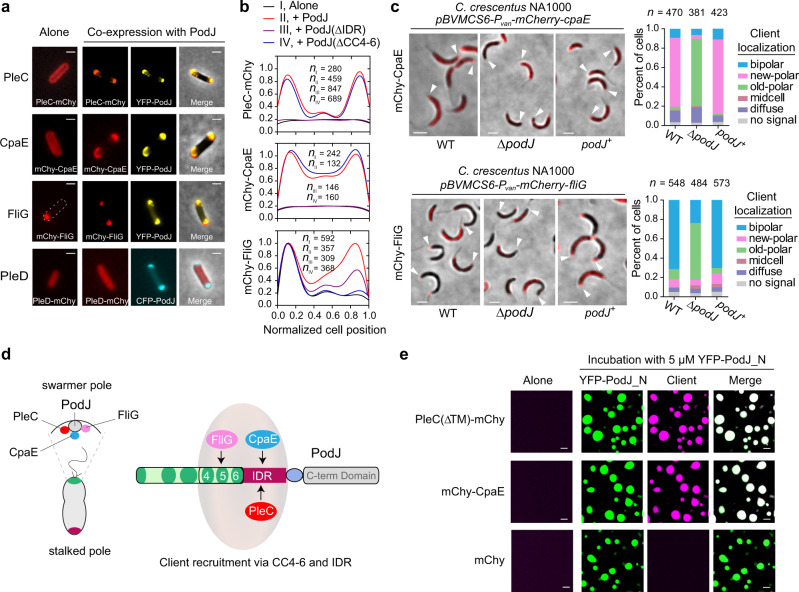
Fig. 4. PodJ recruits client proteins via the LLPS-related domains.
a Identification of PodJ clients in E. coli. Three out of 23 proteins (PleC, CpaE, and FliG) were identified by co-expressing them with PodJ to observe their subcellular localization changes in E. coli. PleD is shown as a negative control. b Quantitative analyses of the client signal along the cell lengths. These client proteins were expressed alone or co-expressed with PodJ (or PodJ variants) using the same induction concentration in E. coli. Data were normalized with the highest intensity as 100% in protein localized strains. c Confirmation of the recruitment for CpaE and FliG to the new cell poles by PodJ in C. crescentus. mCherry-CpaE and mCherry-FliG were expressed in wild-type (WT), ΔpodJ, or podJ complementary strains (podJ+: C. crescentus ΔpodJ, xylX::Pxyl-podJ), respectively, to observe their subcellular localization changes. Quantifications of the client localization patterns are shown in the right panels. White arrows, new cell poles. d Schematic illustration of the client protein recruitment by PodJ. IDR is required for the recruitment of PleC and CpaE while CC4–6 is required for the recruitment of FliG. e PodJ recruits PleC and CpaE via LLPS in vitro. YFP-PodJ_N was incubated with 10 µM PleC(∆TM)-mCherry or mCherry-CpaE for 15 min before imaging. The mCherry was used as a negative control. All scale bars, 2 µm. Source data are provided in the Source Data file.