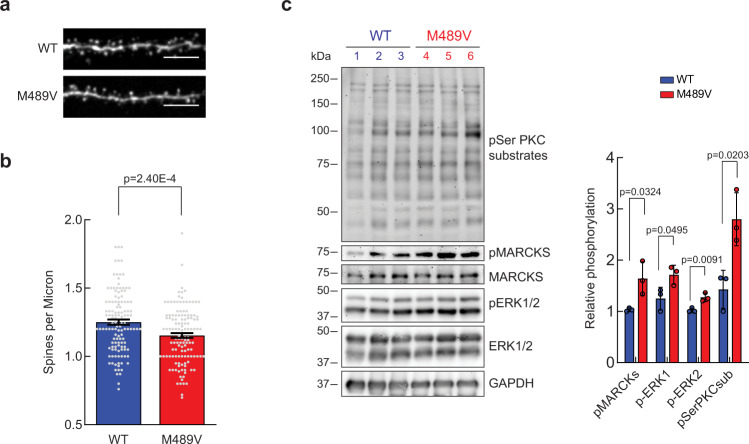
Fig. 2. The AD-associated PKCα M489V mutation reduces spine density and increases PKC substrate phosphorylation in the hippocampus.
a Representative immunofluorescence image of dendritic segments from hippocampal neurons injected with Alexa Fluor® 594 Hydrazide to follow neuronal projections (dendritic segment = 20 µm in length, scale bar 5 µm). n = 129 dendritic segments from 6 mice of each genotype were analyzed. b Average number of spines per micron in neurons isolated from 4–5-month-old WT or littermates M489V PKCα homozygous male mice (n = 6 mice of each genotype). Spines were counted in separate spine segments (10–25 µm in length). Data show a spine density reduction of ~10%, from 1.25 ± 0.02 spines/µm to 1.15 ± 0.02 spines/µm in the M489V mice. n = 129 dendritic segments (over 1500 spines) were analyzed. Error bars show standard error of the mean. (p = 2.40E-4 using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test). c Left. Immunoblots of lysates of hippocampi obtained from WT mice (lanes 1–3, blue) or M489V mice (lanes 4–6, red). Right. Relative phosphorylation represents the densitometric analyses of the western blot phosphorylation signal and the total antibody signal of the indicated substrates. pERK1/2 (T202/Y204 for ERK1 and T185/Y187 for ERK2) and pMARCKS (S159/S163) signal was normalized to total ERK1/2 and total MARCKS signal respectively, and phospho-Ser PKC substrates signal was normalized to its GAPDH loading control. Data were normalized to the WT1 values, and normalized data from the depicted western blots were plotted as average normalized intensity ± SEM (p values were determined using a two-tailed Student’s t test). Data are representative of n = 3 biologically independent experiments. Source data and uncropped blots are provided in the Source Data file.